(1)
Department of Radiology, John H Stroger Jr Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL, USA
Venous Thrombosis
Diagnosis
Acute Deep Vein Thrombosis
Imaging Findings
Ultrasound:
1.
Acute DVT can be sonolucent, spongy, loosely attached to the vessel wall, have an expanded vessel lumen and with no collaterals.
2.
Chronic DVT is more echogenic, attached to a vein wall; veins are irregular and smaller, and with collaterals.
3.
No color flow in complete occlusion and minimal peripheral flow around thrombus in incomplete occlusion.
4.
Spectral Doppler ultrasound shows absence of flow in complete occlusion and spontaneous and continuous flow with absent or dampened respiratory phasicity in incomplete occlusion.
CT:
Filling defect in the vein in CETC

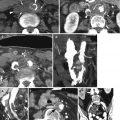
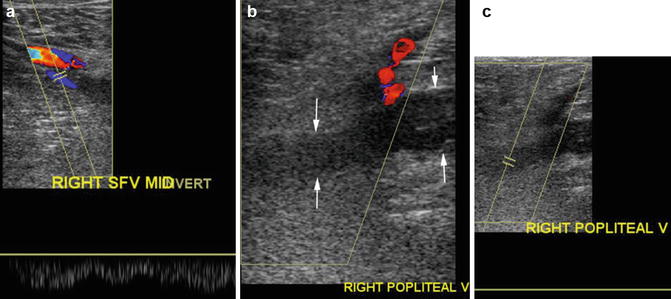
Fig. 2.1
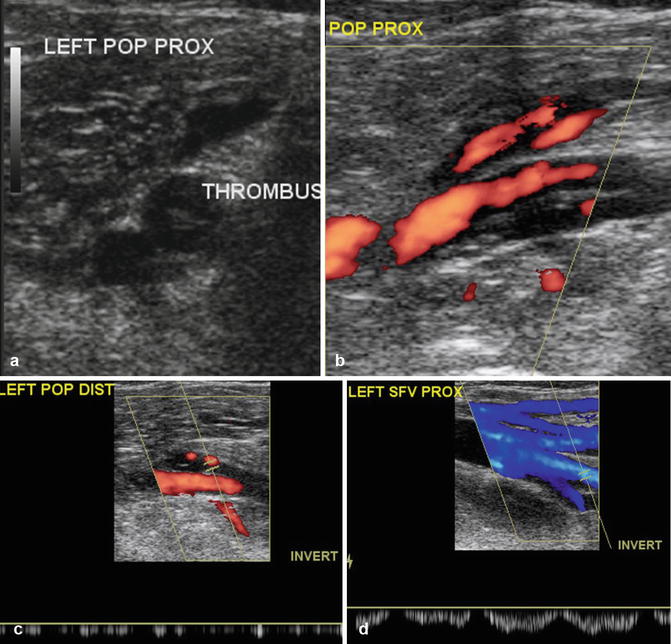
Ultrasound of thrombus in the popliteal vein. Ultrasound of (a) the mid-superficial vein shows color flow and spontaneous phasic flow. (b) The popliteal vein shows echogenic thrombus distending the vein with no color flow (arrows). Flow is seen in the popliteal artery. (c) Absence of spectral flow in the popliteal vein

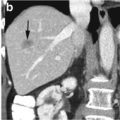
Fig. 2.2
Acute thrombus in the popliteal vein. Axial CECT (a, b) shows thrombus completely filling and distending the popliteal vein and its bifurcation (arrows) with edema in surrounding adipose tissue in the popliteal fossa

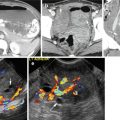
Fig. 2.3
Ultrasound of a nonocclusive central thrombus. (a) Transverse grayscale US shows echogenic central thrombus in the popliteal vein. (b) Longitudinal color Doppler sonogram of the popliteal vein shows reduced antegrade flow around the thrombus. (c) Spectral study shows continuous flow with no respiratory phasicity. (d) Normal antegrade flow in the superficial vein with spectral waves showing normal respiratory phasicity
Diagnosis
Thrombus in the Inferior Vena Cava
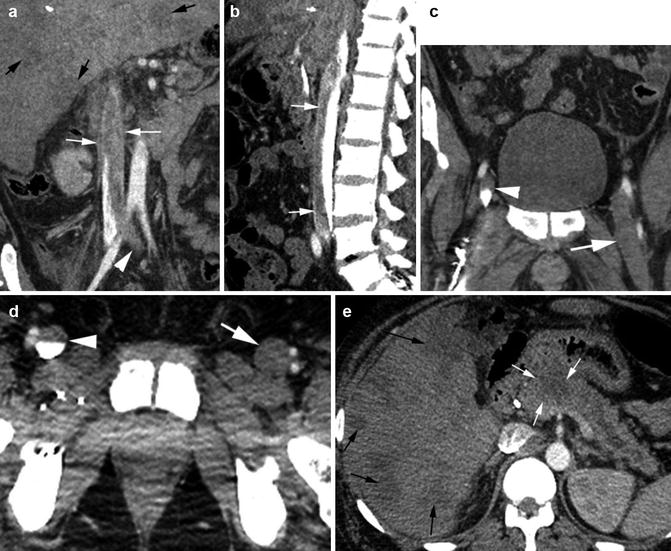

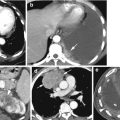
Fig. 2.4
Thrombus IVC with pancreatic carcinoma. CECT (a) coronal reformatted image shows thrombus in the IVC (thin white arrow) extending to the left common iliac vein (arrowhead). (b) Sagittal reformatted image shows thrombus contrast level with thrombus floating above the contrast. (c, d) Coronal and axial CT of the pelvis shows thrombus completely distending the left femoral vein (arrow) and partially filling the right femoral vein (arrowhead). (e) Axial CT shows low-density mass at head of the pancreas (white arrows) obstructing the pancreatic duct and diffuse nodular liver metastasis (black arrows also in a)
Diagnosis
Thrombus in the Superior Mesenteric Vein
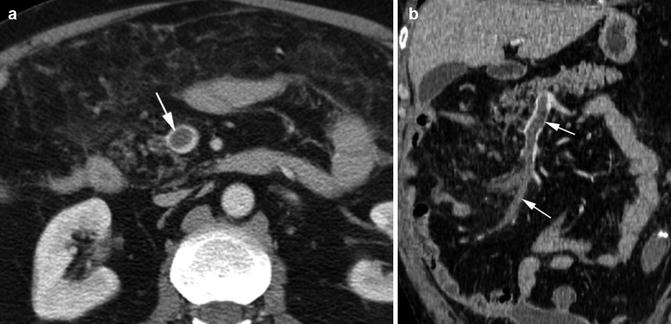
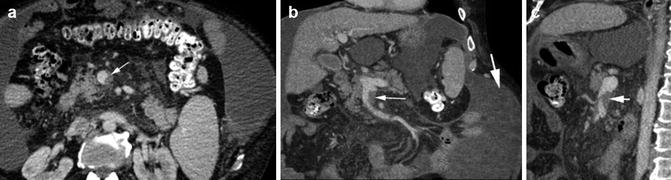

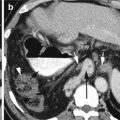
Fig. 2.5
Thrombus in the superior mesenteric vein—acute. (a, b) Axial and coronal reformatted CECT shows acute thrombus in SMV in a patient with recent bowel surgery. The vein is distended by the thrombus with peripheral rim of contrast flow (arrows) proximally. The distal vein is completely thrombosed

Fig. 2.6
Thrombus in the SMV—chronic. History of cirrhosis and hemoperitoneum. (a–c) CECT axial, coronal, and sagittal reformatted images show eccentric chronic thrombus in distal SMV (thin arrow). High-density hemorrhagic ascites is distending the abdomen (thick arrow)
Diagnosis
Bilateral Gonadal Vein Thrombus
Imaging Findings
1.
Dilated gonadal veins bilaterally distended with thrombus.
2.
Thin rim of contrast flow at the periphery.
3.
Veins are at the anterior and medial aspect of the psoas muscles.
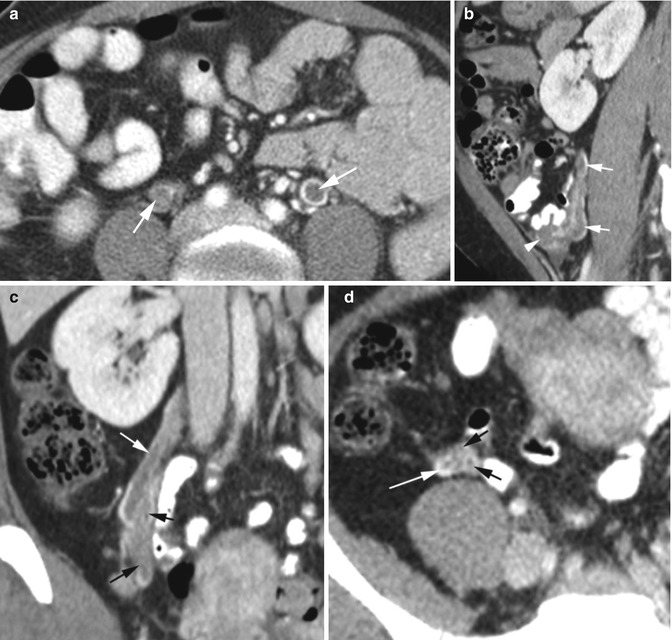
Fig. 2.7
Thrombus in gonadal veins. Patient 1: CECT (a) axial image shows bilateral gonadal vein thrombus (arrows) with rim of contrast around the thrombus. Patient 2: (b) Sagittal reformatted image shows thrombus in the right ovarian vein (arrows) extending from the ovary (arrowhead). (c, d) Coronal and axial CT shows thrombus in multiple ovarian venous plexus (black arrows) which unite higher with the main ovarian vein (white arrow)
Diagnosis
Renal Vein Thrombus
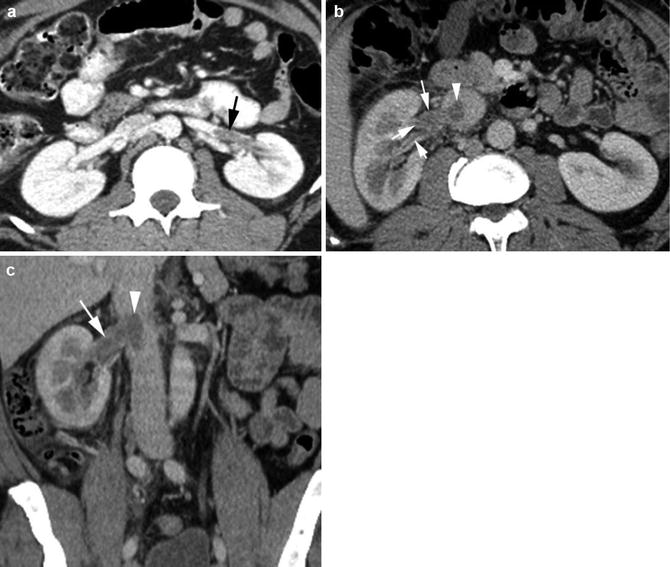

Fig. 2.8
Renal vein thrombus. Patient 1: HIV positive with parvovirus infection, severe anemia, and left flank pain. (a) Axial CT shows thrombus in distal left renal vein (arrow). Patient 2: right flank pain. (b, c) Axial and coronal reformatted CT shows thrombus in the right renal vein and its branches (arrows) extending to the IVC (arrowhead). Ureteral and bladder washes were negative for cancer
Diagnosis
Chronic DVT
Imaging Findings
1.
Grayscale ultrasound shows echogenic thrombus adherent to the wall of the vein.
2.
Color Doppler shows irregular thickening and filling defect of the wall with no luminal filling defect.
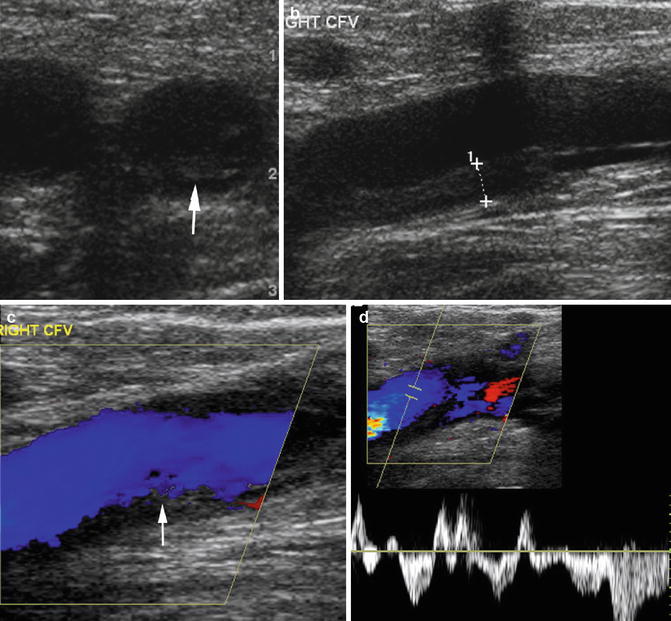
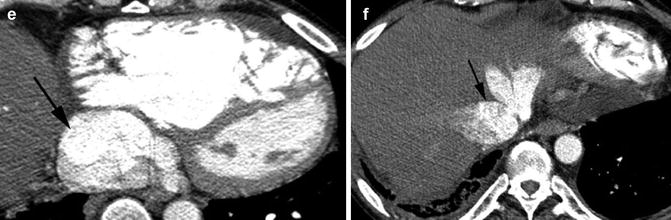
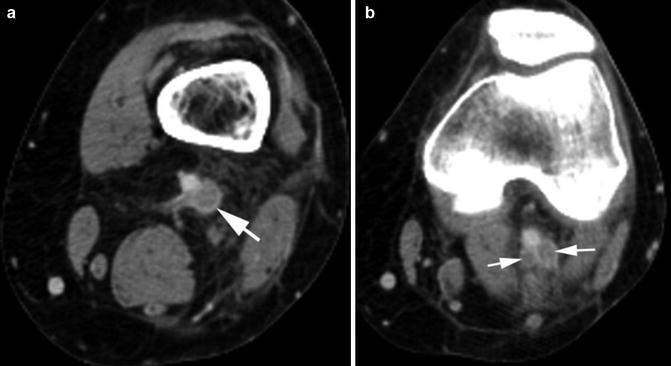
Fig. 2.9
Chronic DVT. (a, b) Transverse and longitudinal views of grayscale ultrasound of the CFV shows echogenic thrombus adherent to the inferior wall of the CFV (arrow in a, caliper in b). (c) Color Doppler shows no central filling defect of the vein. Irregular wall thickening of the inferior wall of the CFV is again seen (arrow). (d) The spectral wave shows arterial pulsation from tricuspid regurgitation. (e) Axial CT shows dilated IVC (arrow). (f) Axial CT shows reflux of contrast into the hepatic veins (arrow)
Diagnosis
Acute Thrombus in the Internal Jugular Vein
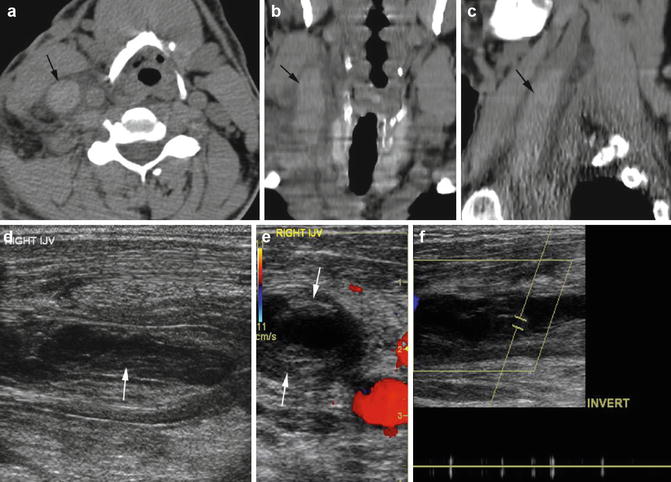
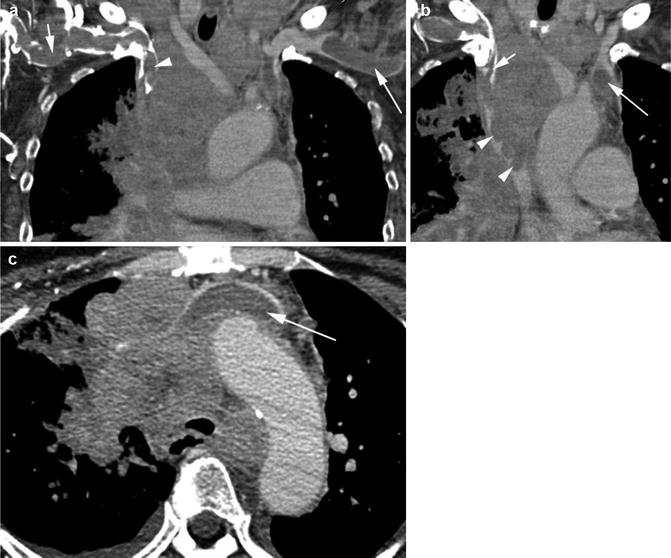

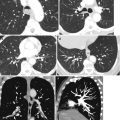
Fig. 2.10
Acute thrombus in the right internal jugular vein—sonolucent and echogenic thrombus. (a–c) Noncontrast axial, coronal, and sagittal reformatted CT shows the right IJ to be distended with acute high-density thrombus (arrow). (d) Longitudinal grayscale ultrasound shows echogenic thrombus at the periphery (arrow also in e) and sonolucent thrombus at the center distending the internal jugular vein. (e) No color flow in transverse color Doppler study. (f) Spectral study shows absent spectral waves

Fig. 2.11
Thrombus brachiocephalic veins. Patient with small-cell lung cancer. CECT (a) coronal reformatted image shows thrombus in the right (short arrow) and left (long arrow) subclavian veins and in the right innominate vein (arrowhead). (b) Coronal reformatted image shows lobulated low-density tumor (arrowheads) invading the SVC causing filling defect of the contrast-filled lumen. Bland thrombus is seen in the right (short arrow) and left (long arrow) innominate veins having lower density than tumor thrombus. (c) Axial CT shows the left innominate vein obstructed by the mediastinal mass and distended by low-density bland thrombus (arrow)
Diagnosis
Thrombus in the Right Pulmonary Vein
Imaging Features
1.
Elongated filling defect in the right pulmonary vein
2.




Infarctions in the spleen and both kidneys
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree