45 Ophthalmic Artery
F. Goetz, A. Giesemann
The practical importance of an anastomosis between the ophthalmic and middle meningeal artery is that branches of the external and internal carotid artery anastomose. The frequency of the origin of the middle meningeal artery from the ophthalmic artery seems to reflect racial differences, for instance, in skulls of people from Papua the foramen spinosum is absent in approximately 10%.1–4
45.1 Connections between the Ophthalmic and Middle Meningeal Arteries

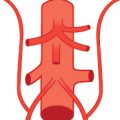
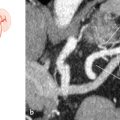
Fig. 45.1 “Normal” situation: only a minor anastomosis between the ophthalmic and middle meningeal arteries (96%). Schematic (a) and X-ray angiography (b), lateral view, three frames after internal carotid artery injection. The middle meningeal artery in b originates from the ophthalmic artery; the patient has an occipital arteriovenous malformation. 1 Ophthalmic artery; 2 middle meningeal artery; 3 anterior cerebral artery; 4 internal carotid artery.

Fig. 45.2 Large anastomosis: the ophthalmic artery originates with comparably strong roots from the internal carotid and middle meningeal arteries (<1%). Schematic.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree