28 Popliteal Artery
T. Rodt, M. Lee
Normally the popliteal artery divides at the upper border of the popliteal muscle. If the division is proximal to this border, it is called a high division. The anterior tibial artery runs anteriorly to the popliteal muscle and corresponds to the profound popliteal artery of most mammals. Only in primates is this vessel replaced by the more superficially positioned popliteal artery. An inter-osseous artery is very rarely found along the interosseous membrane; this artery differs from the popliteal artery.1–5
In addition to anomalies of the main branches of the popliteal artery,6,7 there are many more varieties of the smaller side branches (the genicular and sural arteries). For example, common origins of the superior medial genicular and the descending genicular arteries as well as the superior lateral and the median genicular arteries are frequent. Both upper and lower arteries of the knee joint only rarely form trunks. The origin of the genicular arteries from the sural arteries has been described.
28.1 Branching of the Popliteal Artery at the Lower Border of the Popliteal Muscle (95%)
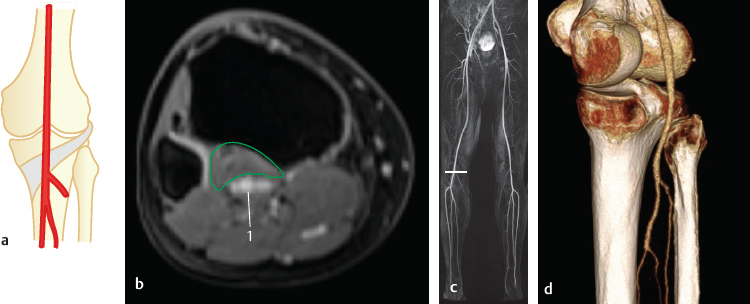
Fig. 28.1 The “normal” situation as described in text books (90%). Schematic (a), axial MR (b), coronal MRA (c) and posteromedial 3D-VR CT (d). The localization of the axial MR slice (b) is marked by the horizontal line in the coronal MRA (c). 1 Popliteal artery. The popliteus muscle is encircled in green.

Fig. 28.2 “Trifurcation” or very short stems of the anterior, posterior tibial, and peroneal arteries (4%). Schematic (a), lateral 3D-MIP CTA with bones removed (b), coronal MIP CTA (c), and posterior 3D-VR CT (d).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree