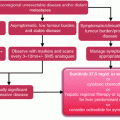
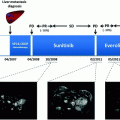
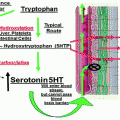
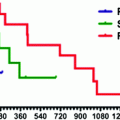
18.
19.
Carracedo A, Ma L, Teruya-feldstein J et al (2008) Inhibition of mTORC1 leads to MAPK pathway activation through a PI3K-dependent feedback loop in human cancer. J Clin Investig 118(9):3065–3074PubMedCentralPubMed
20.
21.
22.
Staal SP (1987) Molecular cloning of akt oncogene and its human homologues AKT1 and AKT2: amplification of AKT1 in a primary human gastric adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci 84:5034–5037PubMedCentralPubMedCrossRef
23.
24.
25.
Ghayouri M, Boulware D, Nasir A et al (2010) Activation of the serine/threonine protein kinase Akt in enteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Anticancer Res 30(12):5063–5067PubMed
26.
27.
Lin J, Sampath D, Nannini MA et al (2013) Targeting activated Akt with GDC-0068, a novel selective Akt inhibitor that is efficacious in multiple tumor model. Clin Cancer Res 19(7):1–13CrossRef
28.
Gloesenkamp CR, Nitzsche B, Ocker M et al (2012) AKT inhibition by tricribine alone or as combination therapy for growth control in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Int J Oncol 40(3):876–888PubMed
29.
Somnay Y, Simon K, Harrison AD et al (2013) Neuroendocrine phenotype alteration and growth suppression through apoptosis by MK-2206, an allosteric inhibitor of AKT, in carcinoid cell lines in vitro. Anti-cancer Drugs 24(1):66–72PubMedCentralPubMed
30.
31.
Hardt M, Chantaravisoot N, Tamanoi F et al (2011) Activating mutations of TOR (target of rapamycin). Genes Cells 16(2):141–151PubMedCentralPubMedCrossRef
32.
Sato T, Nakashima A, Guo L et al (2010) Single aminoacid changes that confer constitutive activation of mTOR are discovered in human cancer. Oncogene 29(18):2746–2752PubMedCentralPubMedCrossRef
33.
34.
Zhou CF, Ji J, Yuan F et al (2011) mTOR activation in well differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: a retrospective study on 34 cases. Hepatogastroenterology 58(112):1–11PubMed
35.
Kasajima A, Pavel M, Darb-Esfahani S et al (2011) mTOR expression and activity patterns in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Endocr Relat Cancer 18:181–192PubMedCrossRef
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree