Pseudomembranous Colitis (Clostridium Difficile)
R. Brooke Jeffrey, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Synonyms: Antibiotic colitis, Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) colitis
Acute inflammation of colon caused by toxins produced by C. difficile bacteria
Imaging
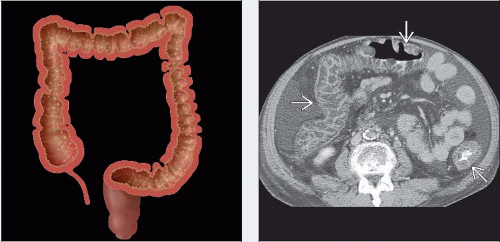
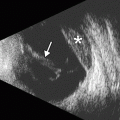
Best diagnostic clue: Marked submucosal edema over long segment of colon
Location
Usually entire colon (pancolitis)
Rectum, sigmoid colon (80-90% of cases)
Thumbprinting
Unusual, wide, transverse bands due to haustral fold thickening
CECT
“Accordion” sign: Trapped enteric contrast between thickened colonic haustral folds
“Target” sign
Pericolonic stranding
Best imaging tool: CECT with oral contrast
Protocol advice: 150 mL IV contrast at 2.5 mL/sec with 5 mm collimation, 5 mm reconstruction interval
Clinical Issues
Elderly at higher risk for developing PMC and recurrent PMC
Clinical profile: Patient with history of watery diarrhea after antibiotic use or hospitalization
Diagnostic Checklist
Check history of antibiotic use or debilitating diseases
Suspect in any hospitalized patient with acute colitis
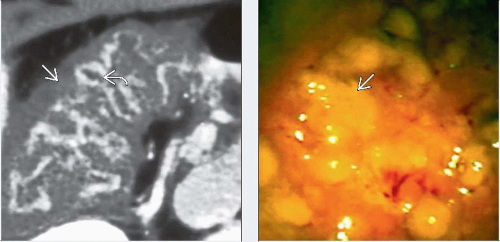 (Left) Axial CECT in a 47-year-old man who had been taking antibiotics for 2 weeks for sinusitis, now presents with a 2-day history of RLQ pain, fever, and concern for appendicitis. Note the marked submucosal edema of the right colon
 and the intense mucosal enhancement and the intense mucosal enhancement  (or “accordion” sign). (Right) Endoscopic photograph of the right colon in the same patient reveals the classic hyperemic mucosa and yellow plaques (or “accordion” sign). (Right) Endoscopic photograph of the right colon in the same patient reveals the classic hyperemic mucosa and yellow plaques  characteristic of pseudomembranous colitis. characteristic of pseudomembranous colitis.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|