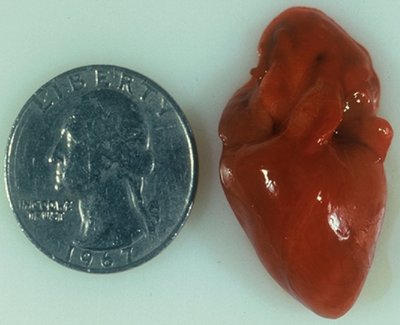
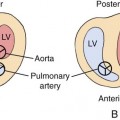
CHAPTER 2 Prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease is important in optimizing obstetrical and neonatal care. Congenital heart disease has been reported to occur in approximately 8 per 1000 live births.1–8 These incidence rates, which are based on live-born infants, underestimate, perhaps considerably, the true incidence of congenital heart disease in the fetus.1,2,4,9 Early fetal loss and stillbirths are often the result of complex heart defects or of chromosomal defects that have an associated heart defect. For this reason, the total congenital heart disease incidence in the fetus has been reported to be as much as five times that found in live-born children.1,9–14 The pooled reported frequency of congenital heart lesions among affected abortuses and stillborn infants shows that ventricular septal defects occur most often (Table 2–1). Coarctation of the aorta and atrial septal defects were also frequently mentioned.15 TABLE 2–1 Frequency of Congenital Heart Lesions among Affected Abortuses and Stillborn Infants Modified from Hoffman JIE: Incidence of congenital heart disease. II: Prenatal incidence. Pediatr Cardiol 1995; 16:155–165. In utero identification of congenital heart disease allows a variety of treatment options to be considered, including delivery at an appropriate facility, termination, and in some cases in utero therapy.5,16–18 Conversely, a normal fetal echocardiogram in the setting of an increased risk factor provides reassurance for both patient and physician. The American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine Technical Bulletin for Performance of the Fetal Cardiac Ultrasound Examination recommends that fetal echocardiographic examinations be performed between 18 and 22 weeks’ gestation.19 It is at this time that optimal image quality, and therefore diagnostic accuracy, is achieved. It should be borne in mind that, even at 18 weeks’ gestation, the fetal heart is a very small structure, and a thorough evaluation may be challenging (Fig. 2–1). Fetal echocardiography performed earlier in pregnancy is feasible in some cases and may be reasonable in a population at risk for a heart defect.7 However, alterations in chamber size, myocardial thickening, and size of the great arteries may occur later in pregnancy.20–22 Therefore a normal appearance of the fetal heart at any time in pregnancy does not exclude congenital heart disease.23 Later in gestation, the echocardiographic examination may be compromised by increased attenuation from the fetal skull, ribs, spine, and limbs and a decrease in amniotic fluid as pregnancy progresses.20,21 Fetal echocardiography requires the use of high-resolution ultrasound equipment.24 Acceptable transducer frequencies range from 5 to 7 MHz, depending on gestational age, maternal body habitus, and the amount of amniotic fluid present. Adequate transducer penetration is also necessary. All equipment used for fetal echocardiography should have M-mode and pulsed Doppler imaging capabilities to provide physiological assessment and color Doppler imaging capabilities to assess spatial and directional information. All these modalities are vital for performing a complete and accurate examination. Additionally, ultrasound equipment with compound imaging capabilities, which allows for off-axis beam steering, can be an asset. The most common indication for performing a fetal echocardiogram is a family history of congenital heart disease (Box 2–1). The risk of occurrence for a fetus varies depending on the type of lesion and the relationship of the fetus to the affected relative. The risk of congenital heart disease in a fetus with an affected sibling is approximately 2% to 4%.25–29 If two or more siblings are affected, this risk increases to about 10% (Table 2–2). When the mother of the fetus is the affected relative, the risk of a heart defect is also approximately 10% to 12%.28,30,31 If the affected relative is the father, the risk is lower (Table 2–3).25–27 If congenital heart disease does recur in families, it is not limited to the same type of defect. TABLE 2–2 Risk of Occurrence for Any Congenital Heart Defect in Siblings Modified from Nora JJ, Fraser FC, Bear J, et al: Medical Genetics: Principles and Practice, 4th ed. Philadelphia, Lea & Febiger, 1994, p 371. TABLE 2–3 Suggested Offspring Occurrence Risk for Congenital Heart Defects Given One Affected Parent (%) Modified from Nora JJ, Fraser FC, Bear J, et al: Medical Genetics: Principles and Practice, 4th ed. Philadelphia, Lea & Febiger, 1994, p 371. Exposure to known cardiac teratogens also increases fetal risk for a heart defect.5,32 The list of substances considered teratogenic is extensive (Table 2–4). The specific risk of occurrence varies with the length and types of exposure and with the specific substance involved. Referrals for fetal echocardiography due to teratogen exposure have decreased over the past decade.8 This most likely represents an increase in awareness of minimizing teratogen exposure in women of reproductive age. TABLE 2–4 Substances Associated with Congenital Heart Disease Data from Sandor GGS, Smith DF, MacLeod PM: Cardiac malformations in the fetal alcohol syndrome. J Pediat 1981; 98:771–773; Nora JJ, Nora AH: Maternal transmission of congenital heart diseases: New recurrence risk figures and question of cytoplasmic inheritance and vulnerability to teratogens. Am J Cardiol 1987; 60:460–463; Stamm ER, Drose JA, Thickman D: The fetal heart. In: Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW (eds): Diagnostic Ultrasound, vol II. St. Louis, Mosby–Year Book, 1991, p 801; Jones KL: Smith’s Recognizable Patterns of Human Malformation, 3rd ed. Philadelphia, WB Saunders, 1988; Nora J, Fraser FC, Bear J, et al: Medical Genetics: Principles and Practice. Philadelphia, Lea & Febiger, 1994; Romero R, Pilu G, Jeanty P, et al: The heart. In: Romero R, Pilu G, Jeanty P, et al. (eds): Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Anomalies. Norwalk, CT, Appleton & Lange, 1988; Taybi H: Radiology of Syndromes and Metabolic Disorders. Chicago, Year Book Medical, 1983; Briggs GG, Freman RK, Yaffe SJ: Drugs in Pregnancy and Lactation. Baltimore, Williams & Wilkins, 1990, pp 1–686; Okuda H, Nagao T: Cardiovascular malformations induced by prenatal exposure to phenobarbital in rats. Congenital Anomalies 2006; 46:97–104; Samren EB, van Duijn CM, Lieve-Christiaens GCM, et al: Antiepileptic drug regimens and major congenital abnormalities in the offspring. Ann Neurol 1999; 46:739–746; Miller LC, Chan W, Litvinova A, et al: Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders in children residing in Russian orphanages: A phenotypic survey. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2006; 30:531–538; Williams LJ, Correa A, Rasmussen S. Maternal lifestyle factors and risk for ventricular septal defects. Birth Defects Res 2004; 70:59–64. Chromosomal abnormalities have been reported to occur in 13% of live-born infants with congenital heart defects.33–36 The incidence of an abnormal karyotype in the fetus with a congenital heart abnormality is approximately 35%.2,37 A study by Nicolaides et al38 in 1993 found chromosomal abnormalities in 101 of 156 (65%) fetuses they identified as having a heart defect. Again, the specific type and occurrence risk of a congenital heart defect varies depending on the chromosomal abnormality. Some abnormal karyotypes have a relatively low association with heart defects, whereas others, such as trisomy 21, are associated with a 40% to 50% occurrence.36–39 The most striking relationship is apparent with trisomy 13 and trisomy 18, in which the association with congenital heart abnormalities is almost 100%.38 Recent literature has reported live-born infants with trisomy 13 and trisomy 18 to have congenital heart disease in 38% and 45%, respectively.40 The discrepancy in these data is probably due to the more recent data consisting only of live births, excluding spontaneous miscarriages or terminated pregnancies. As with teratogenic agents, the list of abnormal karyotypes and syndromes associated with heart defects is extensive (Table 2–5). TABLE 2–5 Chromosome Abnormalities and Syndromes Associated with Congenital Heart Disease
Scanning: Indications and Technique
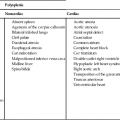
Defect
Frequency (%)
Ventricular septal defect
35.7
Coarctation of the aorta
8.9
Atrial septal defect
8.2
Atrioventricular septal defect
6.7
Tetralogy of Fallot
6.2
Single ventricle
4.8
Truncus arteriosus
4.8
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
4.6
Complete transposition of the great arteries
4.3
Double-outlet right ventricle
2.4
Hypoplasia of the right ventricle
1.7
Single atrium
1.2
Pulmonic stenosis
0.7
Aortic stenosis
0.5
Miscellaneous
10.6
Timing
Equipment
Indications
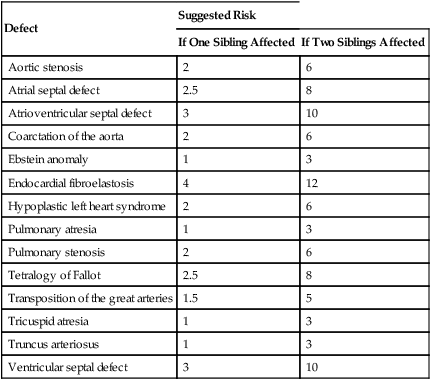
Defect
Suggested Risk
If One Sibling Affected
If Two Siblings Affected
Aortic stenosis
2
6
Atrial septal defect
2.5
8
Atrioventricular septal defect
3
10
Coarctation of the aorta
2
6
Ebstein anomaly
1
3
Endocardial fibroelastosis
4
12
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
2
6
Pulmonary atresia
1
3
Pulmonary stenosis
2
6
Tetralogy of Fallot
2.5
8
Transposition of the great arteries
1.5
5
Tricuspid atresia
1
3
Truncus arteriosus
1
3
Ventricular septal defect
3
10
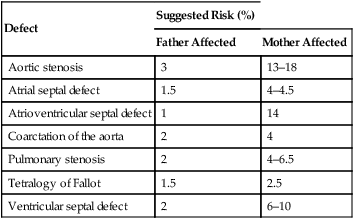
Defect
Suggested Risk (%)
Father Affected
Mother Affected
Aortic stenosis
3
13–18
Atrial septal defect
1.5
4–4.5
Atrioventricular septal defect
1
14
Coarctation of the aorta
2
4
Pulmonary stenosis
2
4–6.5
Tetralogy of Fallot
1.5
2.5
Ventricular septal defect
2
6–10
Substance
Associated Congenital Heart Disease
Alcohol
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, tetralogy of Fallot, pulmonary stenosis, double-outlet right ventricle, dextrocardia
Amantadine
Single ventricle, pulmonary atresia
Amphetamine
Ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, transposition of the great arteries
Azathioprine
Pulmonary stenosis
Barbiturates
Interrupted aortic arch, coarctation
Cannabis
Ventricular septal defect
Carbamazepine
Atrial septal defect
Chlordiazepoxide
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Codeine
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Cortisone
Ventricular septal defect, coarctation
Cyclophosphamide
Tetralogy of Fallot
Cytarabine
Tetralogy of Fallot
Daunorubicin
Tetralogy of Fallot
Dextroamphetamine
Atrial septal defect
Diazepam
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Dilantin (hydantoin)
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, pulmonary stenosis, aortic stenosis
Indomethacin
Ductal constriction
Lithium
Ebstein anomaly, tricuspid atresia, atrial septal defect, mitral atresia, dextrocardia
Methotrexate
Dextrocardia
Oral contraceptives
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Paramethadione
Tetralogy of Fallot
Penicillamine
Ventricular septal defect
Primidone
Ventricular septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation
Progesterone
Ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, truncus arteriosus
Quinine
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Retinoic acid (Accutane)
Ventricular septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, tetralogy of Fallot, truncus arteriosus, double-outlet right ventricle, pulmonary atresia
Thalidomide
Ventricular septal defect, transposition of the great arteries, truncus arteriosus, tetralogy of Fallot, double-outlet right ventricle, pulmonary atresia, atrial septal defect
Trifluoperazine
Transposition of the great arteries
Trimethadione
Ventricular septal defect, transposition of the great arteries, tetralogy of Fallot, hypoplastic left heart syndrome, double-outlet right ventricle, pulmonary atresia, truncus arteriosus, atrial septal defect, aortic stenosis, pulmonary stenosis
Valproic acid
Ventricular septal defect, coarctation, interrupted aortic arch, tetralogy of Fallot, hypoplastic left heart syndrome, aortic stenosis, atrial septal defect, pulmonary stenosis
Warfarin (Coumadin)
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Syndrome
Associated Congenital Heart Disease
Risk (%)
Aase-Smith syndrome
Ventricular septal defect
Achondroplasia
Interrupted aortic arch, coarctation
Acrocephalosyndactyly, type I
Interrupted aortic arch, coarctation
Acrocephalopolysyndactyly, type IV
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Acromicric dysplasia
Atrial septal defect
Acyl-CoA
Cardiomegaly
Adams Oliver syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Alacrima-aptyalism syndrome
Dextrocardia
Alagille syndrome
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis
Antley-Bixler syndrome
Atrial septal defect
33
Apert syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, coarctation, tetralogy of Fallot
10
Arachnodactyly
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Arthrochalasis multiplex congenita
Atrial septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, bicuspid aorta, bicuspid tricuspid valve, dextrocardia, coarctation
Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita
Ventricular septal defect, coarctation, aortic stenosis
Asymmetric crying face
Tetralogy of Fallot, ventricular septal defect
Bardet-Biedl syndrome (Laurence-Moon)
Ventricular septal defect, total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
Beckwith-Wiedeman syndrome
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, cardiomegaly
Beemer lethal malformation syndrome
Tetralogy of Fallot, double-outlet right ventricle
Bernheim syndrome
Cardiomegaly, hypoplastic left heart syndrome, aortic stenosis, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation
Berry-Treacher Collins syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Bixler syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Bourneville-Pringle syndrome
Rhabdomyoma, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation
Bowen-Conradi-Hutterite syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
C syndrome
Atrioventricular septal defect
Campomelic dysplasia
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Cardiac-limb syndrome
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect
85
Cardiofacial syndrome–asymmetric facies
Atrial septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, tetralogy of Fallot
Cardiomelic syndrome
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect
85
Carpenter syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, transposition of the great arteries
3
Cat-eye syndrome (partial trisomy 22)
Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, pulmonary stenosis
40
Cayler syndrome
Atrial septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, right aortic arch, pulmonary stenosis, atrial stenosis
CHARGE (coloboma of the eye, heart anomaly, choanal atresia, retardation, and genital and ear anomalies) syndrome
Atrioventricular septal defect, coarctation, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, truncus arteriosus, double-outlet right ventricle, tetralogy of Fallot, right aortic arch
50
CHILD (congenital hemidysplasia with ichthyosiform erythroderma and limb defects) syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect
CHIME (colobomas, heart defects, ichthyosiform dermatosis, mental retardation, and ear defects or epilepsy) syndrome
Tetralogy of Fallot, transposition of the great arteries
Chondroectodermal dysplasia
Atrial septal defect, single atrium
50
Coffin-Siris (Coffin-Laury) syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Cohen syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
29
Congenital abducens–facial paralysis
Dextrocardia
Congenital facial diplegia
Dextrocardia
Congenital oculofacial paralysis
Dextrocardia
Conradi-Hunermann syndrome (chondrodysplasia punctata)
Ventricular septal defect
Crouzon syndrome
Coarctation
Cryptophthalmos syndrome
Atrial septal defect, truncus arteriosus, ventricular septal defect, transposition of the great arteries, right aortic arch
Cryptophthalmos–syndactyly syndrome
Atrial septal defect, truncus arteriosus, transposition of the great arteries, ventricular septal defect, right aortic arch
DeLange syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, double-outlet right ventricle, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation
29
Dermal faciocardial skeletal syndrome
Atrial septal defect, pulmonary stenosis
Diastrophic dysplasia
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
DiGeorge syndrome (22q)
Ventricular septal defect, coarctation, truncus arteriosus, transposition of the great arteries, tetralogy of Fallot, interrupted aortic arch, double-outlet right ventricle
95
Distichiasis–lymphedema
Truncus arteriosus
95
Duane syndrome
Atrial septal defect
Dysencephalia syndrome
Atrial septal defect
Dyssegmental dysplasia
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Eagle-Barrett syndrome
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, dextrocardia, tetralogy of Fallot, bicuspid aortic valve, bicuspid tricuspid valve
Elfin facies syndrome
Atrial septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, aortic stenosis, mitral regurgitation, ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot
100
Ellis–van Creveld syndrome (chondrodysplasia punctata)
Atrial septal defect, single atrium
Emery-Dreifuss syndrome
Cardiomyopathy
Facioneuro syndrome
Cardiomegaly
Factor V deficiency
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect
Ferrell-Okihiro-Halel syndrome (Ferrell-Okihiro-Halal syndrome)
Atrial septal defect
Fanconi pancytopenia
Atrial septal defect
14
Femoral-facial syndrome
Truncus arteriosus, pulmonary stenosis
Franceschetti-Klein syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect
Franceschetti-Zwahler-Klein syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect
Fraser syndrome
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, truncus arteriosus, transposition of the great arteries, right aortic arch
Friedreich ataxia
Pulmonary stenosis, asymmetrical septal hypertrophy
Gardner-Silengo-Wachtel syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Geleophysic dwarfism
Atrial septal defect, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, aortic insufficiency, pulmonary stenosis, mitral stenosis
Golabi-Ito-Hall (X-linked mental retardation)
Atrial septal defect
Goldenhar syndrome
Tetralogy of Fallot, atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, coarctation, interrupted aortic arch, right aortic arch
Goodman syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Halarz syndrome
Atrial septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, dextroposition, ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, absent right pulmonary artery
Hand-heart syndrome
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect
85
Heart-hand syndrome, type IV
Ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, single atrium
Hirschsprung disease
Interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, ventricular septal defect, mitral stenosis
Holt-Oram syndrome
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect
85
Hydrolethalus syndrome
Truncus arteriosus, ventricular septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect, hypoplastic left heart syndrome, double aortic arch
Hypogonadotropic syndrome
Atrial septal defect
Hypertelorism-hypospadias syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
25
Hypertelorism-microtia-facial clefting
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Hypertrichosis osteochondrodysplasia
Aortic stenosis
Ivemark syndrome
Atrial isomerism, atrioventricular septal defect, complete heart block
Johanson-Blizzard syndrome
Truncus arteriosus, atrial septal defect, transposition of the great arteries, single atrium, total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
Kabuki make-up syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
32
Kallman syndrome
Atrial septal defect, Ebstein anomaly, right aortic arch
Kallman–deMorsier syndrome
Atrial septal defect, Ebstein anomaly, right aortic arch
Kartagener syndrome
Dextrocardia
Keutel syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis
Klippel-Feil syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, transposition of the great arteries, total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome
Cardiomegaly
Kneist-like dysplasia
Atrial septal defect
Larsen syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Laurence-Moon syndrome (Bardet-Biedl)
Ventricular septal defect, total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
Leopard syndrome
Pulmonary stenosis, complete heart block, cardiomyopathy
Lethal facial-cardiomelic dysplasia
Dilated right heart, single atrium, interrupted aortic arch, transposition of the great arteries, ventricular septal defect, mitral atresia
Locking digits–growth defect
Atrial septal defect
Lutembacher syndrome
Atrial septal defect, mitral stenosis, cardiomegaly
Majewski syndrome
Atrial septal defect
Marfan syndrome
Dilated aortic root
95
Marshall-Smith syndrome
Atrial septal defect
McDonough syndrome
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, aortic stenosis, pulmonary stenosis
Meckel syndrome
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect
Meckel-Gruber syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, coarctation, pulmonary stenosis
Mesomelic dysplasia
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Miller-Dieker syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Mobius syndrome
Dextrocardia
Mutchinick syndrome
Atrial septal defect, pulmonary stenosis
Myhre syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Nakago syndrome
Cardiomegaly, hypertrophic hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Neurofibromatosis
Atrial septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, coarctation, interrupted aortic arch, ventricular septal defect, complete heart block, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Noonan syndrome
Pulmonary stenosis, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, total anomalous pulmonary venous connection, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, atrial stenosis, tetralogy of Fallot
65
Oculoauriculovertebral anomaly
Interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, right aortic arch
Okihiro syndrome
Atrial septal defect
Opitz syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Opitz-Kaveggia FG syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Oropalatal-digital syndrome
Interrupted aortic arch, coarctation
Pallister-Hall syndrome
Atrioventricular septal defect
Pena-Shokeir syndrome
Interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, transposition of the great arteries, right ventricular hypertrophy
Pentalogy of Cantrell
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, total anomalous pulmonary venous connection, pulmonary stenosis, tetralogy of Fallot, ectopia cordis
Pierre Robin syndrome
Atrial septal defect
9
Poland syndrome
Tetralogy of Fallot, atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation
Polydactyly chondrodystrophy, types 1 and 2
Transposition of the great arteries, truncus arteriosus, transposition of the great arteries, double-outlet right ventricle
Polysyndactyly–cardiac malformations
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect, single ventricle
Potter syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Prune-belly syndrome
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis
Pulmonary venolobar syndrome
Atrial septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, dextroposition, ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, absent right pulmonary artery
Radial-renal syndrome
Ventricular septal defect
Radial-renal-ocular syndrome
Atrial septal defect
Rolland-Desbuquois syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect
25
Rubinstein-Taylor syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
36
Saldino-Noonan syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Salonen-Herva-Norio syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect, truncus arteriosus, hypoplasia of left ventricle, double aortic arch
Schinzel-Giedion syndrome
Atrial septal defect
Scimitar syndrome
Atrial septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, dextroposition, ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, absent right pulmonary artery
Seckel syndrome
Ventricular septal defect
Shone syndrome
Interrupted aortic arch, coarctation
Short rib polydactyly syndrome, type II
Atrial septal defect
Short rib polydactyly syndrome (non-Majewski type)
Transposition of the great arteries, double-outlet left ventricle, double-outlet right ventricle, atrioventricular defect, hypoplasia of right ventricle
Siegler syndrome
Ventricular septal defect
Silverman-Handmaker-type dwarfism
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Situs inversus viscerum
Atrial septal defect
Silver syndrome
Tetralogy of Fallot, ventricular septal defect
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect
Sofer syndrome
Ventricular septal defect
Sternal-cardiac malformations association
Atrial septal defect
Stevenson syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
40
Sturge-Weber anomaly
Coarctation
Thanatophoric dysplasia
Interrupted aortic arch, coarctation
Thalassemia major
Cardiomyopathy
Thrombocytopenia–absent radius
Atrial septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, dextrocardia
33
Treacher Collins syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect
Tuberous sclerosis
Rhabdomyoma, angioma, coarctation, interrupted aortic arch
VACTERL (vertebral abnormalities, anal atresia, cardiac abnormalities, tracheoesophageal fistula or esophageal atresia, renal agenesis and dysplasia, and limb defects) syndrome
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome, ventricular septal defect
50
Varadi syndrome
Interrupted aortic arch, coarctation
Venolobar syndrome
Atrial septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, dextroposition, ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, absent right pulmonary artery
Velocardiofacial syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, right aortic arch
80
Verma-Naumoff syndrome
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Waardenburg syndrome
Ventricular septal defect
Weaver syndrome
Ventricular septal defect
Weill-Marchesani syndrome
Pulmonary stenosis, ventricular septal defect
William syndrome
Aortic stenosis, pulmonary stenosis, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, interrupted aortic arch, mitral regurgitation, tetralogy of Fallot, coarctation
100
Williams-Beuren syndrome
Interrupted aortic arch, coarctation, aortic stenosis, pulmonary stenosis, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, mural regurgitation, tetralogy of Fallot
100
Zellweger syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect
Chromosome Abnormalities
Monosomy 1q
Ventricular septal defect
Monosomy 1q4
Ventricular septal defect, truncus arteriosus, pulmonary atresia, pulmonary stenosis
Monosomy 2q
Atrial septal defect, coarctation, interrupted aortic arch, ventricular septal defect
Monosomy distal 4q
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Monosomy 5p
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Monosomy 5q (interstitial)
Coarctation, interrupted aortic arch
Monosomy 6q (proximal)
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Monosomy 7p2
Ventricular septal defect, hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Monosomy 7q1
Coarctation
Monosomy 8p2
Ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis
Monosomy 9 (mosaic)
Coarctation, interrupted aortic arch
Monosomy 10q2
Ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis
Monosomy 11q
Ventricular septal defect, truncus arteriosus
50
Monosomy 13q
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
55
Monosomy 14q
Atrial septal defect
Monosomy 14q
Atrial septal defect
Monosomy 16q
Ventricular septal defect
Monosomy 18q
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
25
Monosomy 22
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Monosomy 22q (DiGeorge syndrome)
Ventricular septal defect, coarctation, truncus arteriosus, transposition of the great arteries, tetralogy of Fallot, interrupted aortic arch, double-outlet right ventricle
95
Partial monosomy 9p
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Partial monosomy 11p
Tetralogy of Fallot, cardiomyopathy
Partial trisomy 10q
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
50
Partial trisomy 14q
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Partial trisomy 22 (Cat-eye syndrome)
Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect
40
T 20p syndrome
Ventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot
Tetrasomy 9p
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Trisomy 1q25-1q32
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Trisomy 1q32-QTER
Truncus arteriosus
Trisomy 2q
Ventricular septal defect, aortic stenosis
Trisomy 3q2
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
33
Trisomy distal 4q
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Trisomy 4p
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Trisomy 5p
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Trisomy 5p3
Ventricular septal defect
Trisomy 5q3
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Trisomy 6p2
Ventricular septal defect
Trisomy 7p2
Ventricular septal defect
Trisomy 7q2-3
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Trisomy 8 (mosaic)
Ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect
50
Trisomy 9 (mosaic)
Ventricular septal defect, coarctation, double-outlet right ventricle, atrial septal defect
50
Trisomy 9p
Ventricular septal defect
26
Trisomy 10p
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Trisomy 11p
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Trisomy 12p
Ventricular septal defect
Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)
Ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, dextroposition, hypoplastic left heart syndrome, atrioventricular septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, coarctation, interrupted aortic arch
90+
Trisomy 13q
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Trisomy 14p
Ventricular septal defect
Trisomy 14 (mosaic)
Tetralogy of Fallot
90
Trisomy 15q2
Ventricular septal defect
Trisomy 16p
Atrial septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot
Trisomy 16q
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)
Bicuspid aortic valve, pulmonary stenosis, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect, double-outlet right ventricle, coarctation, interrupted aortic arch
99+
Trisomy 18p
Coarctation, interrupted aortic arch
Trisomy 19q
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Trisomy 20p
Congenital heart disease (unspecified)
Trisomy 20ptr ≈ q11
Ventricular septal defect
Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)
Atrioventricular septal defect, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, tetralogy of Fallot, coarctation, interrupted aortic arch, pulmonary atresia
50
Trisomy 22
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect
67
Triploidy
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect
Turner syndrome (45X)
Bicuspid aortic valve, aortic stenosis, coarctation, ventricular septal defect, atrial septal defect, atrioventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis, interrupted aortic arch, total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
20+
4p− (Wolf syndrome)
Atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect
40
5p− (cri-du-chat syndrome)
Ventricular septal defect
30
9p−
Ventricular septal defect, pulmonary stenosis
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access