11
Spleen
Splenic Artery Aneurysm
Overview
 Most common visceral artery aneurysm
Most common visceral artery aneurysm
 Third most common intra-abdominal aneurysm after abdominal aortic aneurysm and iliac artery aneurysm
Third most common intra-abdominal aneurysm after abdominal aortic aneurysm and iliac artery aneurysm
 Risk factors include collagen vascular disorder, portal hypertension, pregnancy, trauma, pancreatitis, and fibrodysplasia
Risk factors include collagen vascular disorder, portal hypertension, pregnancy, trauma, pancreatitis, and fibrodysplasia
Signs and Symptoms
 Mostly asymptomatic
Mostly asymptomatic
 May have vague left upper quadrant or epigastric pain
May have vague left upper quadrant or epigastric pain
 If ruptured, patient will display signs of hypovolemic shock along with abdominal distension
If ruptured, patient will display signs of hypovolemic shock along with abdominal distension
Diagnosis
 CT angiography, MRI/MRA, or abdominal ultrasound
CT angiography, MRI/MRA, or abdominal ultrasound
Treatment/Management
 Operative management if ≥2 cm, pregnancy, anticipated pregnancy, pseudoaneurysm, expanding aneurysm, or if patient is symptomatic
Operative management if ≥2 cm, pregnancy, anticipated pregnancy, pseudoaneurysm, expanding aneurysm, or if patient is symptomatic
 Operative management includes aneurysmectomy, partial splenectomy, endovascular embolization, or stent graft exclusion of the aneurysm
Operative management includes aneurysmectomy, partial splenectomy, endovascular embolization, or stent graft exclusion of the aneurysm
RADIOLOGY
 Plain film findings
Plain film findings
• Splenic artery calcifications may be seen in the left upper quadrant
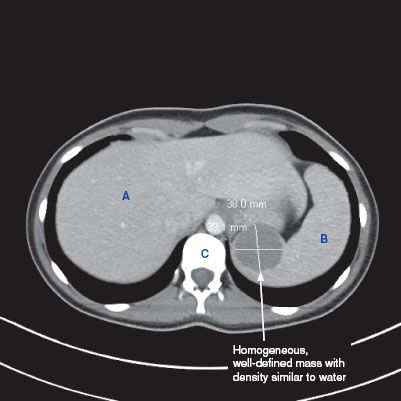
 CT findings (Fig. 11.1)
CT findings (Fig. 11.1)
• Focal dilation of the splenic artery, usually containing wall calcifications
• Enhancement equal to that of the aorta
• May contain mural thrombus
FIGURE 11.1 A–F
A. Liver
B. Kidney
C. Spleen
D. Descending aorta
E. Vertebra
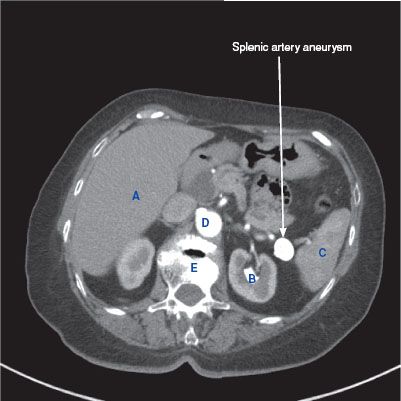
FIGURE 11.1 A

FIGURE 11.1 B
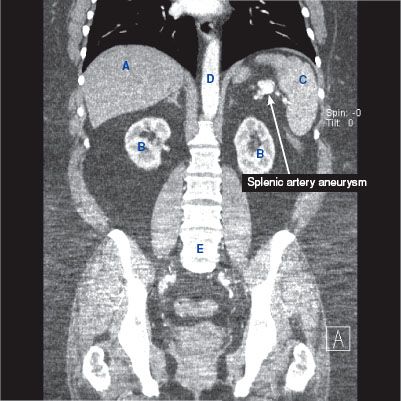
FIGURE 11.1 C
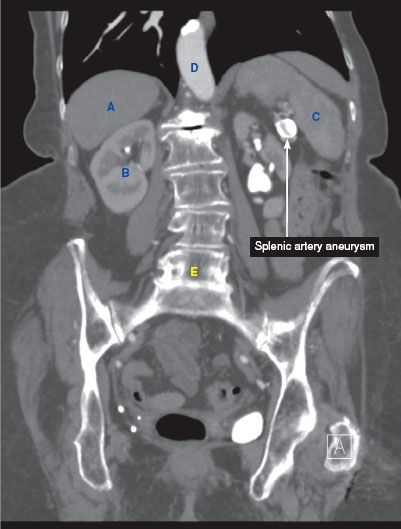
FIGURE 11.1 D
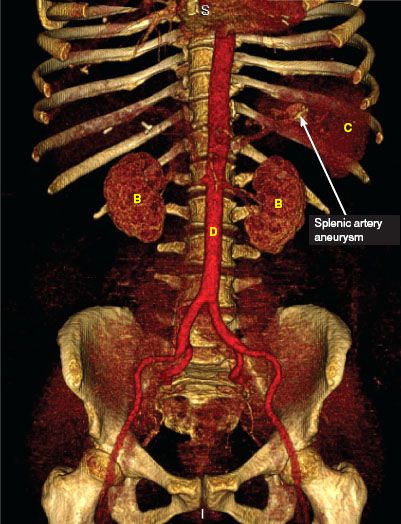
FIGURE 11.1 E

FIGURE 11.1 F
Splenic Cyst
Overview
 Categorized into the following:
Categorized into the following:
• Nonparasitic cyst (two types):
 Congenital—true epidermoid cyst (has an epithelial lining)
Congenital—true epidermoid cyst (has an epithelial lining)
 Pseudocyst—acquired from trauma
Pseudocyst—acquired from trauma
• Parasitic cyst: From echinococcal infection
Signs and Symptoms
 Typically asymptomatic and found incidentally
Typically asymptomatic and found incidentally
 If cyst is large enough, patient will experience abdominal pain with left-sided scapular or shoulder pain, early satiety, nausea or vomiting, weight loss
If cyst is large enough, patient will experience abdominal pain with left-sided scapular or shoulder pain, early satiety, nausea or vomiting, weight loss
Diagnosis
 Ultrasound—can establish the presence of a cystic lesion
Ultrasound—can establish the presence of a cystic lesion
 CT—nonenhancing cystic lesion within the spleen
CT—nonenhancing cystic lesion within the spleen
 Peripheral or septal calcifications may be seen
Peripheral or septal calcifications may be seen
 Serology for echinococcal antibodies
Serology for echinococcal antibodies
Treatment/Management
 Nonparasitic cysts
Nonparasitic cysts
• Asymptomatic—observation
• Symptomatic—unroofing, partial splenectomy
 Parasitic cyst—splenectomy
Parasitic cyst—splenectomy
• Avoid spillage of cyst contents intraoperatively (results in anaphylactic shock)
RADIOLOGY
 Plain film findings (Fig. 11.2 D)
Plain film findings (Fig. 11.2 D)
• May see a calcifications outlining the cyst
 US findings (Fig. 11.2 E)
US findings (Fig. 11.2 E)
• Pseudocysts may show internal echoes from debris
• Pseudocysts may show echogenic foci with posterior acoustic shadowing due to calcification
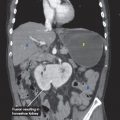
 CT findings (Fig. 11.2 A,B,C)
CT findings (Fig. 11.2 A,B,C)
• Homogeneous, well-circumscribed, fluid attenuation
• No internal enhancement
• Cyst wall calcification may be present
• May contain internal septations
 MRI findings
MRI findings
• Homogeneous, well-circumscribed, T2 hyperintense due to fluid
• Pseudocysts have variable signal intensity on T1-weighted images due to the presence of blood or proteinaceous material
FIGURE 11.2 A–E
A. Liver
B. Spleen
C. Vertebra
D. Kidney
E. Psoas muscle
F. Stomach
G. Descending aorta
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree