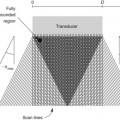
49 Sural Nerve Block
The sural nerve forms from branches of the common peroneal (lateral) and tibial (medial) components of the sciatic nerve. Although the sural usually receives both contributions, anatomic variation in its composition is common.1
The sural nerve lies adjacent to the small saphenous vein within the subcutaneous tissue of the lateral leg. The sural nerve provides sensory innervation to the lateral foot.2 Because it is a sensory nerve, the sural nerve is sometimes used for biopsy or harvest. Although subcutaneous infiltration is an effective means of blocking the distal sural nerve, more proximal block may be indicated in patients with infection or edema of the foot.
Suggested Technique
Key Points
| Sural Nerve Block | The Essentials |
|---|---|
| Anatomy | The SuN emerges between the medial and lateral heads of the GC. |
| The SuN lies adjacent to the SSV within SQ tissue of the lateral leg. | |
| The SuN is about 2.5 mm in diameter. |