50 Tibial Nerve Block
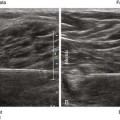
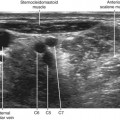
The tibial nerve is the largest branch of the sciatic nerve and the largest nerve for the ankle block. It provides sensory innervation to the heel and to the sole of the foot. The tibial nerve divides into the medial calcaneal, medial plantar, and lateral plantar branches near the ankle.1 In some subjects the takeoff of the medial calcaneal branch from the tibial nerve can be imaged above the ankle joint.
Edema or infection often makes routine ankle block ineffective or contraindicated.2 However, tibial nerve imaging can be difficult in some surgical patients with peripheral vascular disease because vascular landmarks for the nerve are not present. Tibial nerve block in the leg avoids the footdrop that occurs with more proximal popliteal block of the sciatic nerve. This can be an advantage for ambulatory surgery patients.