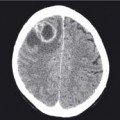
30.1 Liver metastases
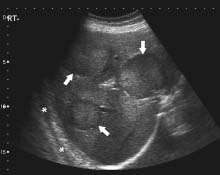
Multiple well-defined round lesions are seen in the liver (arrows). This was the first evidence of metastatic disease in this patient with a history of breast cancer. Depth in centimetres is shown down the side of the image. (*) diaphragm
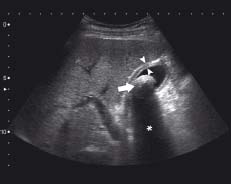
The gall bladder contains a large gallstone (arrow) with a distal acoustic shadow (*) (see Chapter 3). The gall bladder is thick-walled (arrowheads). These are the typical ultrasound features of cholecystitis
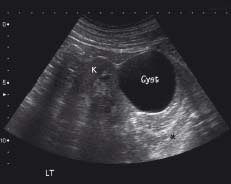
There is a cyst arising from the cortex of the kidney (K). This is causing acoustic enhancement artefact (*) (see Chapter 3). This cyst is simple in nature with a thin wall. The presence of features such as septation and calcification would be associated with an increased risk of malignancy
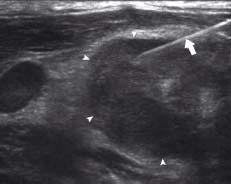
Ultrasound is an excellent tool for guided fine-needle aspiration (FNA). Here the FNA needle (arrow) can be seen passing into an enlarged lymph node (arrowheads). Fine movements and capillary action provide a small cytology sample which is examined microscopically
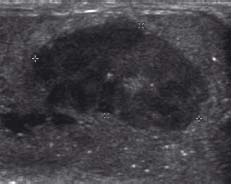
An ovoid irregular mass within the testis has been marked (crosses). Ultrasound is highly sensitive for detecting lesions in the testes. No preoperative FNA or biopsy was required for this lesion and the entire testis was removed. The lesion proved to be a seminoma, the commonest type of testicular malignancy
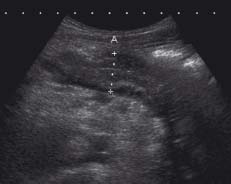
Measurement A (2.5 cm) is of a thick-walled segment of bowel thought to be the appendix in this patient who presented with right lower quadrant pain and tenderness. A subsequent CT demonstrated terminal ileitis. The normal appendix measures less than 10 mm but is thickened and non-compressible if inflamed
Liver lesions
The liver on US appears as a large solid structure lying in the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and has a uniform echotexture. It is supplied by the portal vein and hepatic artery, and is drained by the hepatic veins. Abnormalities of the liver include:
- Metastatic disease – these are focal areas of low, high or mixed echogenicity.
- Cysts –

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree