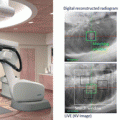
Fig. 10.1
Absolute overall displacement for six nonpatient subjects immobilized with the thermoplastic mask system. No repositioning was made for the whole test period (From Ref. [8])
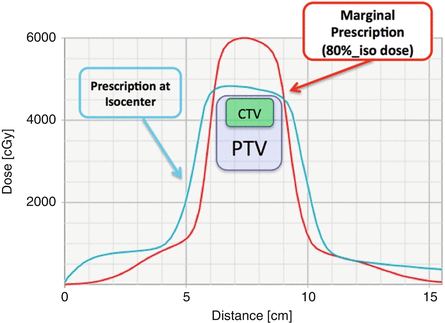
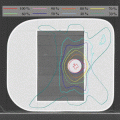
So far, prescribe dose to the point such as isocenter or the reference point based on ICRU guideline was frequently used for SBRT treatment planning. On the other hand, prescribe dose to the isodose line covers target, which is common prescription for stereotactic irradiation for intracranial case, is also applied to SBRT cases. Figures 10.2 and 10.3 shows the comparison between two different prescription method (48 Gy/4 fractions) for HCC case. For the maginal prescription, 80 % isodoseline was adjusted to fit the PTV and isodose line is normalized to the dose to isocenter. As shown in Fig. 10.3, the marginal prescription gives rapid dose fall-off around PTV than iso center prescription, so that the required accuracy of target localization is more strict for marginal prescriptions.
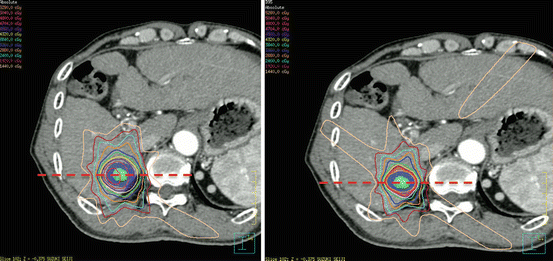

Fig. 10.2
Comparison of 2D dose distribution between two types of treatment of planning for liver SBRT, prescription at isocenter (left) and marginal prescription (right). 1D dose profiles of dashed line are shown in Fig. 10.3
10.5 Evidence of Effectiveness About IGRT and Treatment Quality
Zelefsky et al. reported the retrospective comparison of the outcomes of a cohort of patients treated with definitive IGRT using implanted fiducial markers to the outcomes in a cohort treated with the same dose and margins with IMRT without daily target position correction (non-IGRT) [9]. In this report they compare the toxicity and tumor control outcomes of these two patient cohorts. Their findings showed the lower incidence of late urinary toxicity and improved early biochemical tumor control for high-risk patients in the IGRT-treated patients compared with the non-IGRT cohort (Fig. 10.4). Note that IGRT and respiration-motion management techniques not only for the accuracy of target localization, but also the normal tissue sparing.
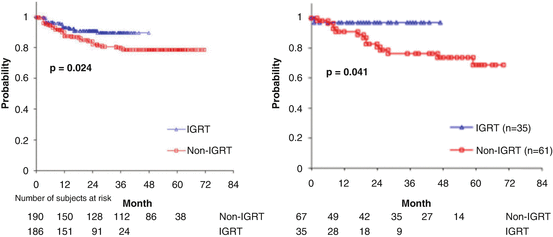

Fig. 10.4
Left: Comparison of actuarial likelihood of grade 2 or higher late urinary toxicity for patients treated with image-guided radio- therapy (IGRT) to 86.4 Gy vs. intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Right: Comparison of prostate specific antigen relapse-free survival outcomes between patients treated with image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT) to 86.4 Gy and those treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy to the same dose level (Captured from Ref. [9])
In clinical trials group of Australia, tirapazamine for advanced head and neck cancer patients of 861 people in 2010: I have reported the results of a phase III trial on adding to cisplatin · radiation therapy (TPZ hypoxic cytotoxins) [10]. Results identify hypoxia, in advanced head and neck cancer patients that have not been selected, added to chemoradiotherapy TPZ not improve overall survival, clinical utility of TPZ, the hypoxia Although is that there is likely to be limited to cases to be confirmed, I would like addressed, “has been posted on the next page of this phase III trial of paper Critical Impact of Radiotherapy Protocol Compliance and Quality in the Treatment of Advanced Head and Neck Cancer: a paper titled Results From TROG 02.02” [11]. In this paper, we secondary analysis on the results of the phase III trial described above, is quantitatively evaluated the effect of radiotherapy quality has on the results of clinical trials, very interesting. Radiation therapy is interrupted cases and was not performed cases removed from the statistics, it is classified 780 cases irradiated least 60 Gy over the four categories. Among them, deviations are expected to affect tumor control rate 87 cases of 11 % was found. While this itself is not in fact be arbitrarily uncommon in clinical trials, and surprised the 2-year survival rate obtained by extracting only the errant case group is 20 % compared to the group without deviating (70 % → 50 %) he that was worse! In other words, radiation therapy QA/QC is, it is suggested that than combined chemoradiotherapy using new drugs is a major factor in ensuring the local control, drug radiotherapy if properly administered it is possible to enhance the effect, the tumor dose insufficient by radiation therapy which means that it can not be compensated with a drug. And, this paper is the last to be summarized in the following sentence. “It is sobering to note that the value of good radiotherapy is substantially greater than the incremental gains that have been achieved with new drugs and/or biologicals.”
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree