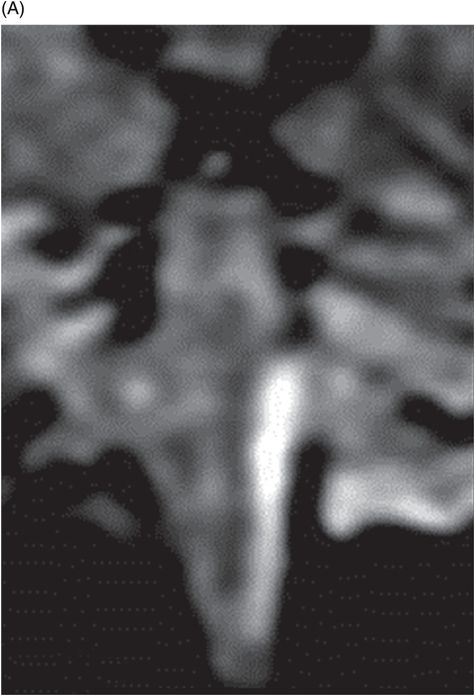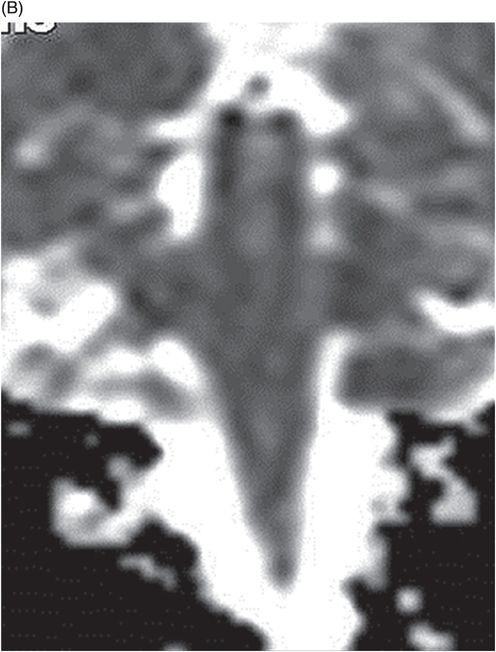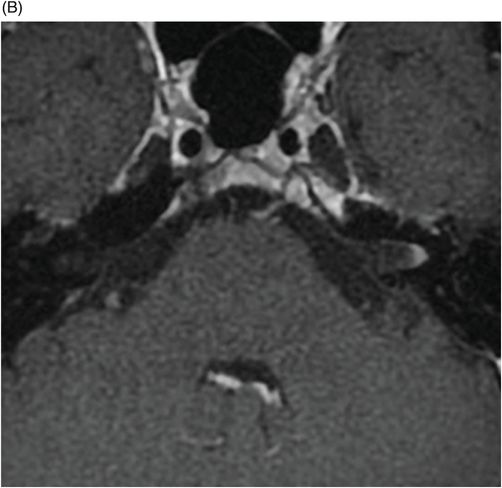
(A–B) Coronal T1WI postcontrast images after digital subtraction through the level of the internal auditory canal.

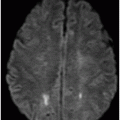
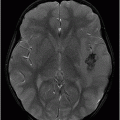
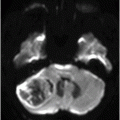
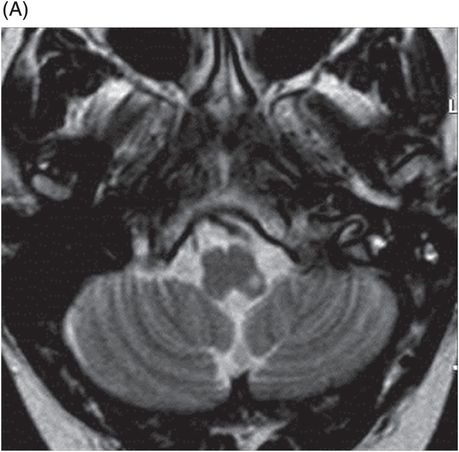
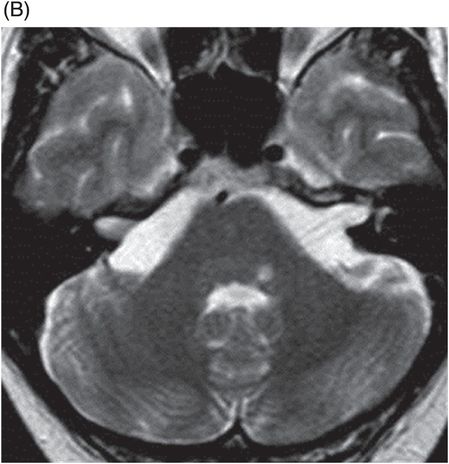
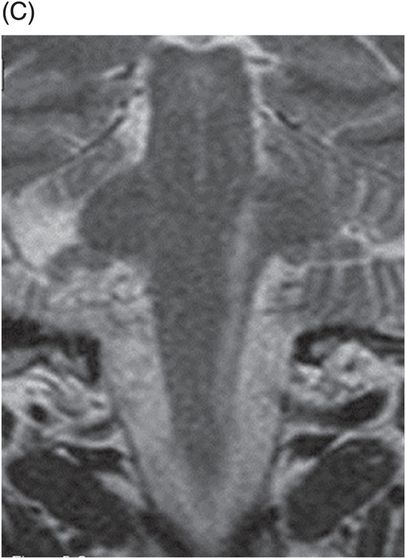
(A–B) Axial T2WI and (C) Coronal T2WI through the brainstem.
Ramsay Hunt Syndrome with Involvement of Spinal Nucleus and Tract of Trigeminal Nerve
Primary Diagnosis
Ramsay Hunt syndrome with involvement of spinal nucleus and tract of trigeminal nerve
Differential Diagnoses
Bell palsy
Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis
Facial nerve schwannoma
Imaging Findings
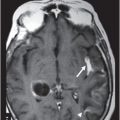
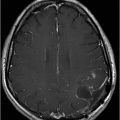
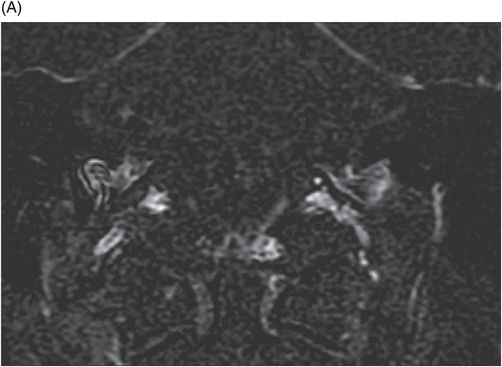
Fig. 36.1: (A–B) Axial T1WI postgadolinium showed important uptake through paramagnetic contrast, in the topography of the facial nerve (CN VII), without characterization of nodular lesions. Fig. 36.2: (A–B) Coronal T1WI postcontrast after digital subtraction showed the enhancement stretched across the temporal and extratemporal path of the left facial nerve to the parotid gland. Fig. 36.3: (A–B) Axial T2WI and (C) Coronal T2WI showed hyperintense signals in the spinal tract of the left trigeminal nerve (CN V). Fig. 36.4: (A) Axial DWI, (B) ADC map, and (C) Coronal T1WI postcontrast images showed a hyperintense lesion without restriction and non-enhancement after gadolinium in the left posterolateral aspect of the pons and the medulla, outlining the nucleus and spinal tract of the ipsilateral trigeminal nerve.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree