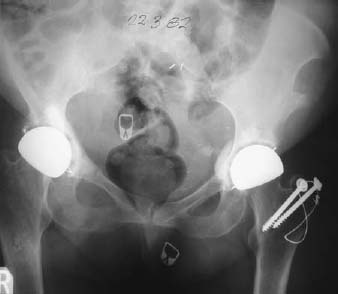
CASE 88 Hema N. Choudur, Anthony G. Ryan, and Peter L. Munk An elderly woman presented with pain in the right groin following a left hip arthroplasty and a greater trochanteric fracture fixation. Prior right hip arthroplasty had been performed several years previously. No abnormality was detected on clinical examination. Figure 88A Plain radiograph of the pelvis (Fig. 88A) shows fractures through the right superior and inferior pubic rami following an arthroplasty. No other fractures are evident in the pelvic bones. Gross demineralization of the bones of the pelvis is evident. Insufficiency fractures of the right pubic rami. A fracture resulting from normal stress on abnormal bone is described as an insufficiency fracture. The abnormality is in terms of a generalized or focal demineralization of the bones, usually secondary to osteopenia. It must be differentiated from a pathologic fracture, which is through a primary or secondary bony lesion. The most common sites of insufficiency fractures are the vertebral bodies. Other sites include the sacral ala, iliac bones, pubic rami, tibia, fibula, and calcaneus. These fractures are more common in women than men, occur in 1 to 5% of any given population, and occur after 60 years of age. When the bony trabaculae are lost, as in osteoporosis, the elasticity of the bone is reduced, resulting in a fracture, when the bone is no longer able to accommodate the stresses. The most common cause of insufficiency fractures is postmenopausal or “senile” osteoporosis. Other causes include
Insufficiency Fracture
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Etiology
Pathophysiology
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


