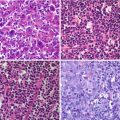
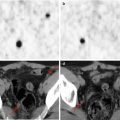
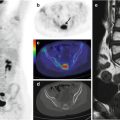
Fig. 17.1
A 9-year-old boy treated for adrenal gland carcinoma. Axial CT with lung window (a), PET (b), and PET/CT fusion (c) images show nonhomogeneous FDG uptake in the right lung, corresponding to a metastasis
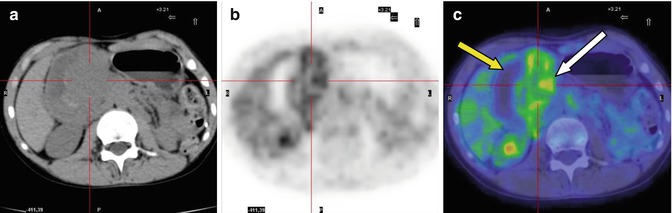
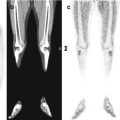
Fig. 17.2
Same patient during treatment with imatinib for disease relapse in the abdomen. Axial CT with abdominal window (a), PET (b), and PET/CT fusion (c) images show extensive nonhomogeneous FDG fixation in the (right) abdomen (white arrow in c). The area without FDG metabolism corresponds to the necrotic component of the lesion (yellow arrow in c)
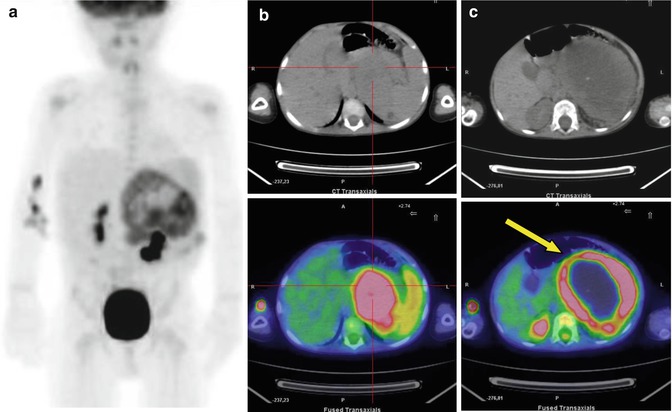
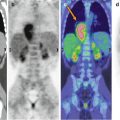
Fig. 17.3
A 3-year-old boy with adrenal gland carcinoma. Maximum intensity projection (a) and CT and PET/CT fusion images (b, c) show different aspects of the abdominal lesion. Note the broad, non-metabolizing central area, corresponding to necrosis (yellow arrow in c)