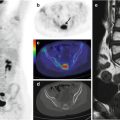
Fig. 35.1
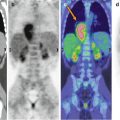
Axial (a) PET, (b) CT, and (c) PET/CT images. A focal uptake is evident in the uncinatus process of the head of the pancreas (red arrow in a and c)
Case 2: Diffuse Form
A 2-year-old boy with severe perinatal hypoglycemia (first episode 2 days after his birth) was referred for an 18F-DOPA–PET/CT study. His clinical characteristics suggested a diagnosis of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia. The patient was responsive to diazoxide (7 mg/kg/day) but he had a mild cognitive delay secondary to recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia in the neonatal period.
PET/CT demonstrated the homogeneous uptake of 18F-DOPA, suggesting a diffuse form of congenital HI. The SUVmax values in the pancreas were 1.5 in the head, 1.4 in the body, and 1.4 in the tail (SUVr of each pancreatic region <1.2) (Fig. 35.2). The patient is currently under medical therapy with good control of his glucose levels.
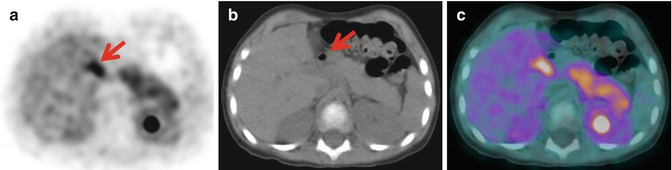
Fig. 35.2
Axial (a) PET, (b) CT, and (c) PET/CT images show homogeneous pancreatic uptake of 18F-DOPA, suggesting a diffuse form of congenital hyperinsulinism. The arrow (in a and b) indicates physiologic activity in the biliary duct
Teaching Points
PET/CT with 18F-DOPA is a simple and effective tool to differentiate between focal and diffuse forms of HI with high accuracy. This information cannot be obtained by other noninvasive diagnostic procedures [6]. When a focal area of intense 18F-DOPA uptake is detected in the pancreatic region, a sequentially coregistered contrast-enhanced CT is useful to guide the surgeon in limited resection of the focal lesion by means of the vascular map. The SUV ratio completes the visual analysis and allows discrimination between focal and diffuse disease forms [4, 7].
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree