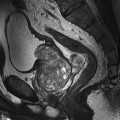
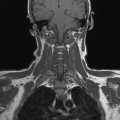
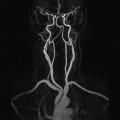
7 Contrast enhancement is extremely valuable in many disease processes including tumours, inflammation and infection. Although these pathologies contain a high water content and are often visualized in T2-weighted images, sometimes, there is insufficient contrast between the lesion and surrounding tissue. In addition, T1-weighted images demonstrate a higher SNR and are therefore advantageous, but water and pathology are commonly isointense in these sequences. Therefore, it is sometimes necessary to selectively enhance pathology by administering a contrast agent. As in other diagnostic modalities, MRI contrast media can be classified as either positive or negative agents depending on whether they are required to increase or decrease the amount of signal returned by the tissue in question. Positive agents tend to contain rare earth metal gadolinium as their active ingredient; negative agents have historically contained iron oxide. Only a brief overview is provided here. For a more detailed explanation, please refer to Chapter 11 of MRI in Practice or an equivalent text.
Contrast agents
Introduction
Positive contrast agents
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree