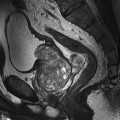
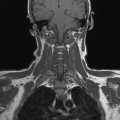
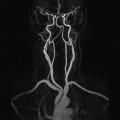
4 This section refers mainly to the Artefact problems subheading discussed under the Image optimization heading considered for each examination in Part 2. The most common flow phenomena are summarized in Table 4.1. Only a brief overview is provided here. For a more detailed explanation, please refer to Chapter 6 of MRI in Practice or an equivalent text. Table 4.1 Artefacts and their remedies The most common types of flow phenomena are: TOF phenomenon occurs because nuclei that move through the slice may receive only one of the RF pulses applied. In GRE sequences, the gradient rephasing is not slice selective, so nuclei produce signal as long as they have been excited at some point and are rephased by the gradient. In a SE sequence, a nucleus may receive the excitation pulse but then exit the slice before the 180° rephasing pulse can be applied. Conversely, it may not be present in the slice when the excitation pulse is applied, and then enter the slice to receive only the 180° pulse. Under these circumstances, the nucleus does not produce a signal. In SE sequences, TOF effects cause either a signal loss or signal enhancement from flowing nuclei, and they are compensated for by using pre-saturation pulses placed between the origin of the flow and the FOV.
Flow phenomena and artefacts
Flow phenomena
Introduction
Artefact
Remedy
Penalty of remedy
Truncation
Increase phase encodings
Increases scan time
Use more than one NEX/NSA
Increases scan time
Phase mismapping
Respiratory compensation
May lose slices
Gating
TR variable
Pre-saturation
May lose slices
GMN
Increases minimum TE
Immobilize patient
None
Use antispasmodic agent
Costly, invasive
Sedation
Invasive, requires monitoring
Chemical shift
Increase bandwidth
Decreases TE
Reduce FOV
Reduces SNR
Use chemical saturation
Reduces SNR
Chemical misregistration
Set TE at multiple of periodicity
None
Aliasing
Oversampling (frequency)
None
Oversampling (phase)
None or increase in scan time depending on system
Enlarge FOV
Reduces resolution
Zipper
Call engineer
Irate engineer!
Magnetic susceptibility
Use SE
Not flow sensitive
Remove metal where possible
None
Shading
Load coil properly
None
Crosstalk
None
None
Cross excitation
Interleaving of slice acquisition
Doubles the scan time
Squaring off of RF pulses
Reduces SNR
Time of flight
Entry slice phenomenon
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree