Musculoskeletal Infection
Thomas H. Berquist
Basic Concepts
Key Facts
Musculoskeletal infections may present with acute rapidly progressive onset or in a more insidious fashion (Table 11-1). Infections may occur from hematogenous spread, spread from a contiguous source, direct implantation (i.e., puncture wound), or after trauma or surgery.
Insidious onset of infection often follows trauma or surgical intervention.
Clinical presentation is dependent on age, virulence of organisms, patient condition, site of involvement, and circulation (Table 11-2).
Early detection and evaluation of the extent of involvement are essential for proper treatment and optimal prognosis.
Imaging of musculoskeletal infection usually requires a multimodality approach.
Radiography: Soft tissue swelling or joint effusion may be the only findings. Significant bone destruction must be present before radiographs are positive.
Radionuclide scans: Bone scanning is sensitive and can detect abnormalities early, but there is less anatomic detail and findings are not specific. Techniques include three-phase technetium-99m-methylene diphosphate, gallium-67-, and indium- or technetium-labeled white blood cell studies, technetium antigranulocyte antibody scans, and positron emission tomography (PET).
TABLE 11-1 INFECTIONS: TERMINOLOGY AND CATEGORIES
Term/Conditions
Clinical/Image Features
Osteomyelitis
Infections in bone and marrow
Bacterial most common
Infective osteitis
Cortical infection. Often associated with marrow or soft tissue infection.
Infective periostitis
Periosteal infection often with marrow and cortex involved
Soft tissue infection
Involves skin, subcutaneous tissues, muscles, tendons, ligaments, fascia, or bursae
Sequestrum
Segment of necrotic bone separated from viable bone by granulation tissue
Involucrum
Living bone around sequestrum
Cloaca
Tract through viable bone
Sinus
Tract from infected region to skin
Fistula
Abnormal communication between two internal organs or internal organs and skin
Brodie abscess
Sharply defined focus of osteomyelitis
Garré sclerosing osteomyelitis
Sclerotic nonpurulent infection with intense periosteal reaction
Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis
Subacute or chronic infection common in children. May be associated with SAPHO.
Synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis and osteitis (SAPHO)
Palmoplantar pustulosis, articular, and hyperostosis and osteitis (SAPHO) periosteal inflammation.
Chronic course involving chest wall, spine, long bones, large and small joints.
SAPHO, synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis.
Computed tomography (CT): cortical and marrow involvement along with sequestra and cloaca detection.
Ultrasound: soft tissue infection, abscess formation, foreign body localization, and aspirations.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI is particularly suited for evaluation of early bone or soft tissue infection. Contrast is superior to CT, and anatomic detail is superior to radionuclide scans. We routinely add contrast-enhanced fat-suppressed T1-weighted images.
Aspiration/biopsy: Regardless of the imaging technique used, joint aspiration or synovial or bone biopsy under fluoroscopic or ultrasound guidance may be required to isolate the organism.
TABLE 11-2 COMMON ORGANISMS IN MUSCULOSKELETAL INFECTIONS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Suggested Reading
Berquist TH, Broderick DF. Musculoskeletal infections. In: Berquist TH, ed. MRI of the musculoskeletal system, 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2006:916–947.
Resnick D. Osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, and soft tissue infection: Mechanisms and situations. In: Resnick D. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders, 4th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2002:2510–2624.
Osteomyelitis
Key Facts
Early diagnosis and management are essential to avoid irreversible bone or articular damage.
Hematogenous osteomyelitis is more common in children than in adults and most frequently involves the lower extremities.
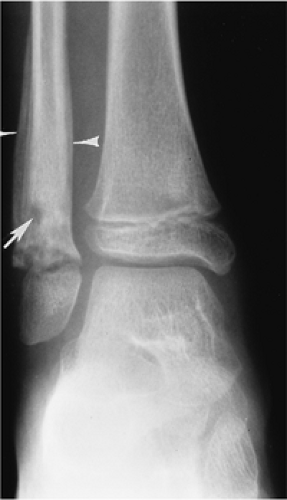
Metaphyseal regions, near the physis, are most commonly involved.
The physis serves a protective function preventing infection from entering the epiphysis and, depending on joint anatomy, the joint from ages 1 to 16 years.
Imaging of osteomyelitis requires a multimodality approach (Table 11-3).
Routine radiographs: may show soft tissue swelling. Bone changes may be inapparent early.
Radionuclide scans: A positive technetium-99m scan is not specific, but a negative scan excludes the diagnosis. Combined indium-111 or technetium-labeled leukocytes and technetium-99m scans are more specific. PET may also be useful.
CT: cortical detail, sequestra, and cloacae
MRI: T1- and T2-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) images are sensitive and can detect changes of infection early. Gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted images are routinely added in our practice. Anatomic detail is superior to radionuclide scans.
TABLE 11-3 IMAGING APPROACHES FOR OSTEOMYELITIS | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||
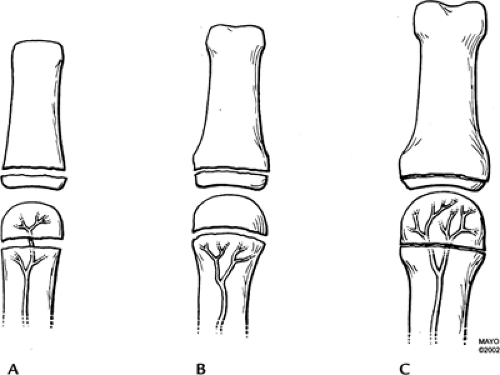 FIGURE 11-1 The vascular supply to the metaphysis and epiphysis in infants (A), children (B), and adults (C). The physis serves a protective function for the epiphysis from ages 1 to 16 years (B). |
Suggested Reading
Bonakdapour A, Gaines VD. The radiology of osteomyelitis. Orthop Clin North Am 1983;14:21–37.
Gold RH, Hawkins RA, Katz BD. Bacterial osteomyelitis: Findings on plain film, CT, MRI, and scintigraphy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1991;157:365–370.
Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis
Key Facts
Characterized by exacerbation and remissions.
May occur at any age but most common in children 5 to 10 years of age.
Patients present with pain, swelling, and tenderness in areas of skeletal involvement.
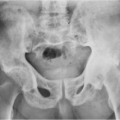
The femoral metaphysis, tibia, and medial clavicles are most commonly involved.
Organisms are difficult to isolate. However, Propionibacterium acne, Corynebacterium, and pneumococci have been identified.
Imaging features show sclerosis of the medial clavicles on radiographs and CT. MR features are nonspecific.
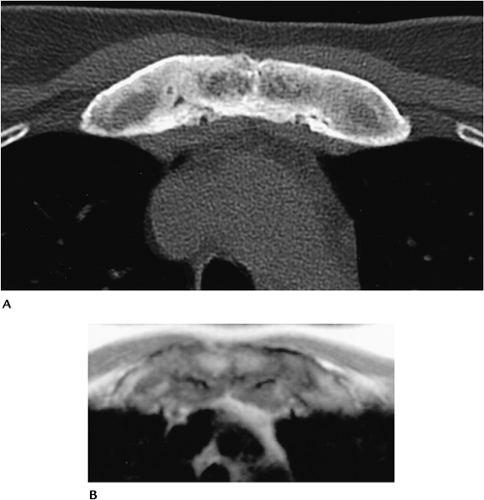 FIGURE 11-3 Axial CT (A) and T1-weighted MR (B) images demonstrate thickening and sclerosis of the medial clavicles and sternocostal junctions. |
Suggested Reading
Demharter J, Bohndorf K, Michl W, et al. Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis: Radiological and clinical investigation in 5 cases. Skel Radiol 1997;26:579–588.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree