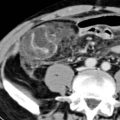
Micronodular pattern: Earliest findings may be subtle peritoneal thickening and hyperenhancement
• MR: Sensitivity of MR is comparable to, or greater than, CT for implants > 1 cm, but limited for small implants
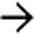 and serosal implants
and serosal implants  .
.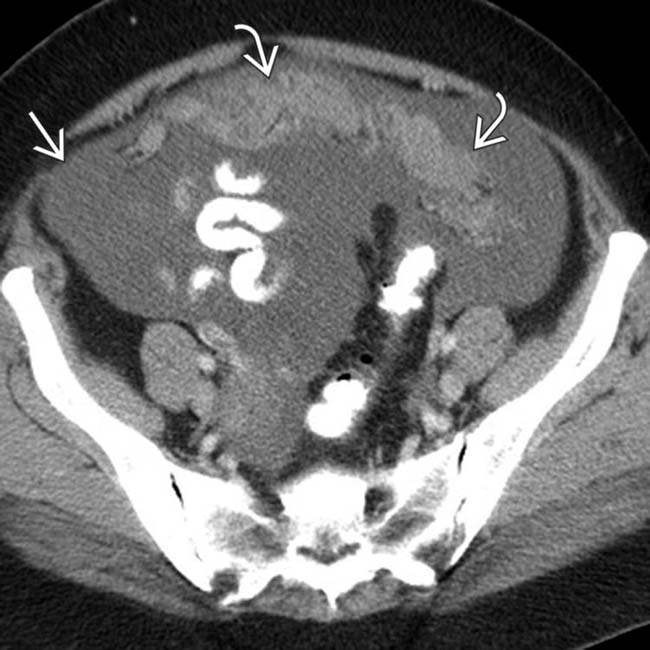
 in the anterior pelvic omentum, compatible with carcinomatosis. Notice the presence of ascites
in the anterior pelvic omentum, compatible with carcinomatosis. Notice the presence of ascites 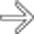 , which is commonly associated with carcinomatosis.
, which is commonly associated with carcinomatosis.
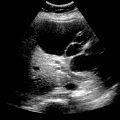
 in the omentum. Although debatable, some sources suggest that MR may have slightly increased sensitivity for carcinomatosis compared to CT.
in the omentum. Although debatable, some sources suggest that MR may have slightly increased sensitivity for carcinomatosis compared to CT.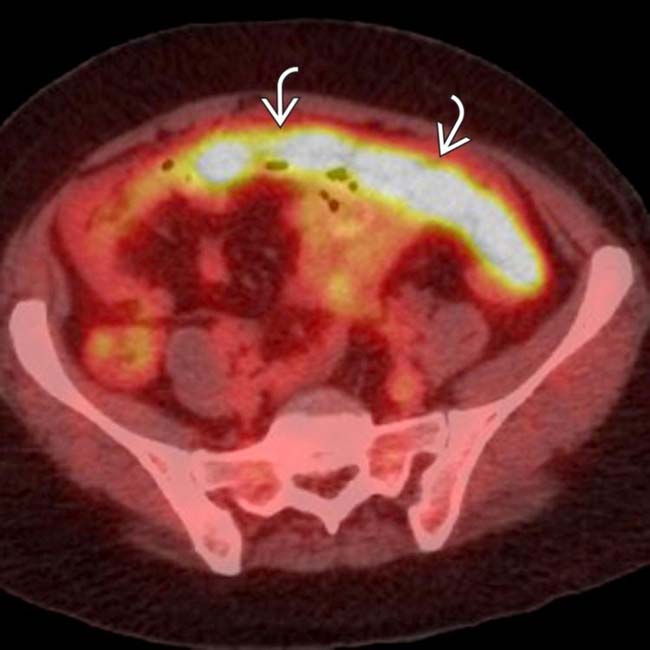
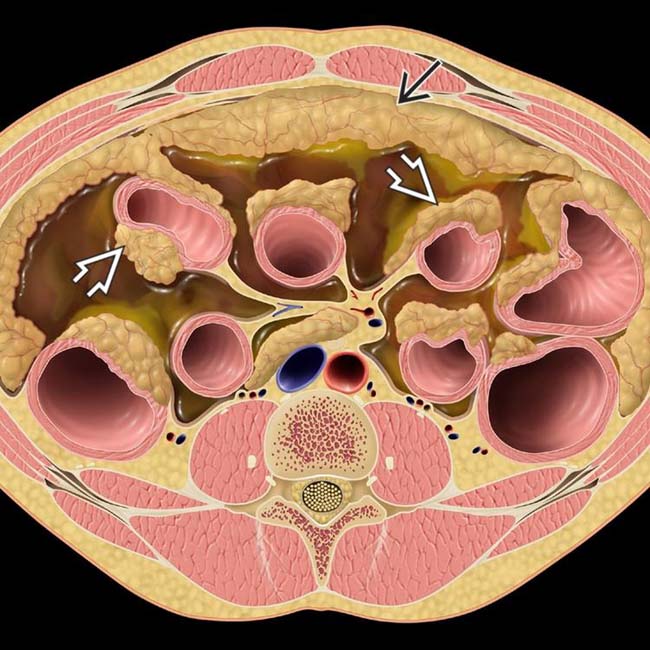
 shows avid FDG uptake. No primary tumor was discovered in this case, and this was found to be peritoneal serous papillary carcinoma.
shows avid FDG uptake. No primary tumor was discovered in this case, and this was found to be peritoneal serous papillary carcinoma.IMAGING
General Features
CT Findings
• CT has limited sensitivity for peritoneal metastases (25-90%), particularly implants measuring < 1 cm (7-50%)
 Particularly difficult to identify tumor implants in certain anatomic locations (liver hilum, bladder dome, subdiaphragmatic positions, mesenteric root, lesser omentum, serosal surface of small bowel)
Particularly difficult to identify tumor implants in certain anatomic locations (liver hilum, bladder dome, subdiaphragmatic positions, mesenteric root, lesser omentum, serosal surface of small bowel)
 Particularly difficult to identify tumor implants in certain anatomic locations (liver hilum, bladder dome, subdiaphragmatic positions, mesenteric root, lesser omentum, serosal surface of small bowel)
Particularly difficult to identify tumor implants in certain anatomic locations (liver hilum, bladder dome, subdiaphragmatic positions, mesenteric root, lesser omentum, serosal surface of small bowel)• 3 primary patterns of carcinomatosis on imaging
 Micronodular pattern
Micronodular pattern
 Micronodular pattern
Micronodular pattern– Omentum often easiest site to appreciate carcinomatosis with nodularity, stranding, and infiltration
• Thickening and nodularity along surface of bowel may reflect tumor implants along serosal surface of bowel
• Tumor implant density will vary based on histology of primary malignancy, with most hypovascular tumors appearing as solid, hypodense soft tissue nodules
 Hypervascular tumors such as renal cell carcinoma may have hyperenhancing peritoneal metastases, which are more conspicuous on arterial phase imaging
Hypervascular tumors such as renal cell carcinoma may have hyperenhancing peritoneal metastases, which are more conspicuous on arterial phase imaging
 Hypervascular tumors such as renal cell carcinoma may have hyperenhancing peritoneal metastases, which are more conspicuous on arterial phase imaging
Hypervascular tumors such as renal cell carcinoma may have hyperenhancing peritoneal metastases, which are more conspicuous on arterial phase imaging• Ascites usually present with loculated ascites common in cases with advanced peritoneal carcinomatosis
MR Findings
• Sensitivity of MR is comparable to, and perhaps even greater than, CT for implants > 1 cm
 Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) offers increased sensitivity for tumor implants, which demonstrate restricted diffusion
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) offers increased sensitivity for tumor implants, which demonstrate restricted diffusion
 Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) offers increased sensitivity for tumor implants, which demonstrate restricted diffusion
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) offers increased sensitivity for tumor implants, which demonstrate restricted diffusion• Caution needed when interpreting SSFSE/HASTE images, as bulk motion of fluid within ascites can lead to signal voids that might be confused for tumor implants
• Tumor implants typically are hypointense on T1WI, intermediate to high signal on T2WI, and demonstrate variable enhancement on T1WI C+ images depending on type of tumor
Nuclear Medicine Findings
• PET/CT
 Offers greater sensitivity relative to PET, CT, or MR in isolation (> 90%)
Offers greater sensitivity relative to PET, CT, or MR in isolation (> 90%)




 Offers greater sensitivity relative to PET, CT, or MR in isolation (> 90%)
Offers greater sensitivity relative to PET, CT, or MR in isolation (> 90%)– May detect occult metastases which were difficult to appreciate on CT or MR due to anatomic location
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree