Small free fluid, edema, and fat stranding in surgical bed with reactive subcentimeter lymph nodes in mesentery
 Mild biliary dilatation, gastrojejunostomy thickening, and pancreatic duct dilatation due to anastomotic edema
Mild biliary dilatation, gastrojejunostomy thickening, and pancreatic duct dilatation due to anastomotic edema Pancreatic duct stent (thin linear radiodensity) often placed during surgery (traversing pancreaticojejunostomy) to ↓ risk of pancreatic fistula
Pancreatic duct stent (thin linear radiodensity) often placed during surgery (traversing pancreaticojejunostomy) to ↓ risk of pancreatic fistula• Common complications
 Abscess: Can be intrahepatic, in pancreatic bed, or in subphrenic, subhepatic, or retroperitoneal spaces
Abscess: Can be intrahepatic, in pancreatic bed, or in subphrenic, subhepatic, or retroperitoneal spaces
 Gastrojejunostomy and hepaticojejunostomy leaks: Suspect when focal fluid collection or ectopic gas in close contiguity to anastomosis
Gastrojejunostomy and hepaticojejunostomy leaks: Suspect when focal fluid collection or ectopic gas in close contiguity to anastomosis
 Postoperative hemorrhage: May be due to bleeding from gastroduodenal artery stump or due to structural abnormality (e.g., pseudoaneurysm)
Postoperative hemorrhage: May be due to bleeding from gastroduodenal artery stump or due to structural abnormality (e.g., pseudoaneurysm)
 Anastomotic strictures: Suspect when progressive biliary or pancreatic ductal dilatation without obstructing tumor at anastomotic site
Anastomotic strictures: Suspect when progressive biliary or pancreatic ductal dilatation without obstructing tumor at anastomotic site
 Delayed gastric emptying: Gastric remnant markedly dilated with large retained ingested material and fluid
Delayed gastric emptying: Gastric remnant markedly dilated with large retained ingested material and fluid
 Abscess: Can be intrahepatic, in pancreatic bed, or in subphrenic, subhepatic, or retroperitoneal spaces
Abscess: Can be intrahepatic, in pancreatic bed, or in subphrenic, subhepatic, or retroperitoneal spaces Gastrojejunostomy and hepaticojejunostomy leaks: Suspect when focal fluid collection or ectopic gas in close contiguity to anastomosis
Gastrojejunostomy and hepaticojejunostomy leaks: Suspect when focal fluid collection or ectopic gas in close contiguity to anastomosis Postoperative hemorrhage: May be due to bleeding from gastroduodenal artery stump or due to structural abnormality (e.g., pseudoaneurysm)
Postoperative hemorrhage: May be due to bleeding from gastroduodenal artery stump or due to structural abnormality (e.g., pseudoaneurysm) Anastomotic strictures: Suspect when progressive biliary or pancreatic ductal dilatation without obstructing tumor at anastomotic site
Anastomotic strictures: Suspect when progressive biliary or pancreatic ductal dilatation without obstructing tumor at anastomotic site Delayed gastric emptying: Gastric remnant markedly dilated with large retained ingested material and fluid
Delayed gastric emptying: Gastric remnant markedly dilated with large retained ingested material and fluid
 , the pancreatic margin
, the pancreatic margin  , and the intestinal margins
, and the intestinal margins  .
.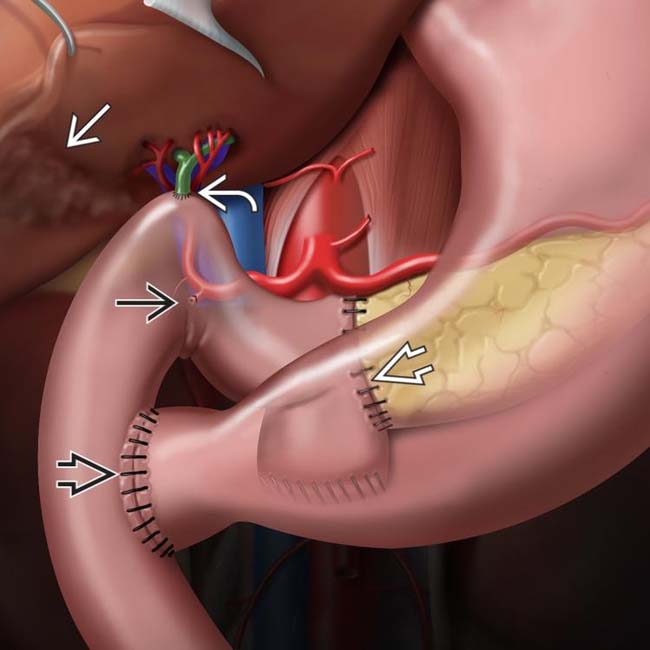
 , choledochojejunostomy
, choledochojejunostomy  , gastrojejunostomy or duodenojejunostomy
, gastrojejunostomy or duodenojejunostomy  , and cholecystectomy
, and cholecystectomy  . The pylorus may be removed or preserved, depending on extent of disease and surgeon preference. Note the ligated gastroduodenal artery
. The pylorus may be removed or preserved, depending on extent of disease and surgeon preference. Note the ligated gastroduodenal artery  .
.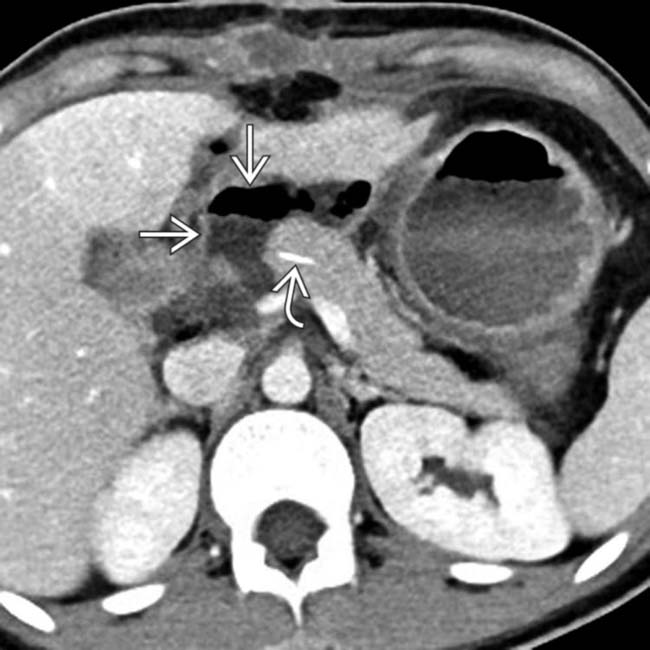
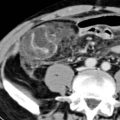
 immediately adjacent to the pancreaticojejunostomy in a patient with an elevated drain amylase, compatible with pancreatic fistula. Note the presence of a pancreatic duct stent
immediately adjacent to the pancreaticojejunostomy in a patient with an elevated drain amylase, compatible with pancreatic fistula. Note the presence of a pancreatic duct stent  .
.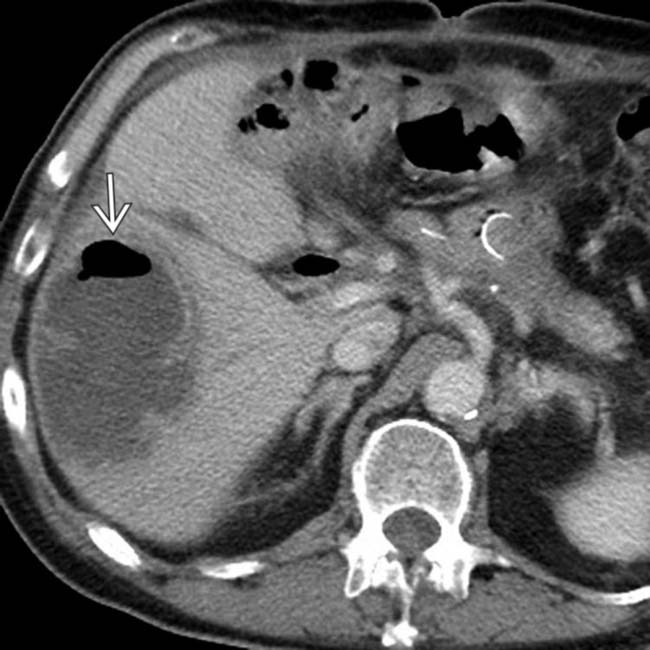
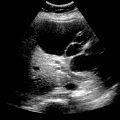
 in the right liver lobe with an internal air-fluid level, compatible with a postoperative hepatic abscess.
in the right liver lobe with an internal air-fluid level, compatible with a postoperative hepatic abscess.IMAGING
General Features
• Best diagnostic clue
 Post Whipple resection: Expected findings include gas in biliary tree, jejunal loop anastomosed to pancreatic neck, gallbladder usually resected
Post Whipple resection: Expected findings include gas in biliary tree, jejunal loop anastomosed to pancreatic neck, gallbladder usually resected
 Post Whipple resection: Expected findings include gas in biliary tree, jejunal loop anastomosed to pancreatic neck, gallbladder usually resected
Post Whipple resection: Expected findings include gas in biliary tree, jejunal loop anastomosed to pancreatic neck, gallbladder usually resected• Surgical procedure determined by location and type of pathology
 Whipple procedure most commonly performed for tumors of pancreatic head, uncinate, and proximal neck
Whipple procedure most commonly performed for tumors of pancreatic head, uncinate, and proximal neck
 Central pancreatectomy performed for low-risk lesions (low malignant potential) in pancreatic neck/body
Central pancreatectomy performed for low-risk lesions (low malignant potential) in pancreatic neck/body
 Enucleation performed for lesions with low malignant potential that are small and exophytic (often utilized for insulinomas)
Enucleation performed for lesions with low malignant potential that are small and exophytic (often utilized for insulinomas)
 Whipple procedure most commonly performed for tumors of pancreatic head, uncinate, and proximal neck
Whipple procedure most commonly performed for tumors of pancreatic head, uncinate, and proximal neck– Classic Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy) involves surgical removal of pancreatic head, gastric antrum, proximal duodenum, and gallbladder
– Pylorus-sparing Whipple procedure, which may theoretically have lower risk of bile reflux, retains pylorus and short segment of duodenum with creation of duodenojejunostomy
 Central pancreatectomy performed for low-risk lesions (low malignant potential) in pancreatic neck/body
Central pancreatectomy performed for low-risk lesions (low malignant potential) in pancreatic neck/body Enucleation performed for lesions with low malignant potential that are small and exophytic (often utilized for insulinomas)
Enucleation performed for lesions with low malignant potential that are small and exophytic (often utilized for insulinomas)CT Findings
• Normal findings immediately after Whipple procedure
 Small free fluid, edema, and fat stranding in surgical bed with reactive subcentimeter lymph nodes in mesentery
Small free fluid, edema, and fat stranding in surgical bed with reactive subcentimeter lymph nodes in mesentery
 Pancreatic duct stent (thin linear radiodensity) often placed during surgery (traversing pancreaticojejunostomy) to ↓ risk of pancreatic fistula
Pancreatic duct stent (thin linear radiodensity) often placed during surgery (traversing pancreaticojejunostomy) to ↓ risk of pancreatic fistula
 Small free fluid, edema, and fat stranding in surgical bed with reactive subcentimeter lymph nodes in mesentery
Small free fluid, edema, and fat stranding in surgical bed with reactive subcentimeter lymph nodes in mesentery Pancreatic duct stent (thin linear radiodensity) often placed during surgery (traversing pancreaticojejunostomy) to ↓ risk of pancreatic fistula
Pancreatic duct stent (thin linear radiodensity) often placed during surgery (traversing pancreaticojejunostomy) to ↓ risk of pancreatic fistula• Complications
 Pancreatic fistula
Pancreatic fistula
 Abscess
Abscess
 Postoperative pancreatitis
Postoperative pancreatitis




 Pancreatic fistula
Pancreatic fistula– Leakage of amylase-rich fluid from pancreatic duct (either at pancreaticojejunal anastomosis or at site of parenchymal injury)
 Abscess
Abscess– Abscesses following Whipple may be intrahepatic, in surgical bed, or in subphrenic, subhepatic, or retroperitoneal spaces
 Postoperative pancreatitis
Postoperative pancreatitisStay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree