Fig. 1
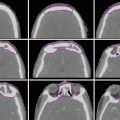
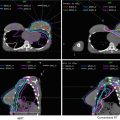
Standard WBRT fields. Conventional opposed lateral fields are rotated slightly off-axis (RAO/LAO) (red/green) to create coplanar anterior field edges which do not diverge into the lenses. (a) Beam’s eye view (RAO) and blocking (diagonal red lines) as defined by graticule measurments X and Y. The inferior field edge is set at C1 with at least 2 cm of flash posteriorly and superiorly. The block begins at the anterior aspect of the C1 vertebral body and is designed to spare nontarget tissues (e.g., parotid glands), while taking care to provide adequate margin on the temporal lobes and cribriform plate (blue). (b) Central axis view showing coplanar anterior field edges. (c) Axial slices demonstrating adequate margin on the cribriform plate (blue) and avoidance of divergent dose through the lenses. (d) Axial slice demonstrating adequate margin on the temporal lobes
The typical treatment technique consists of opposed lateral photon beams. Field design is demonstrated in Fig. 1 and should take care to provide adequate coverage of the cribriform plate and temporal lobes. Figure 2 illustrates variations of the standard WBRT fields to account for differing clinical situations.
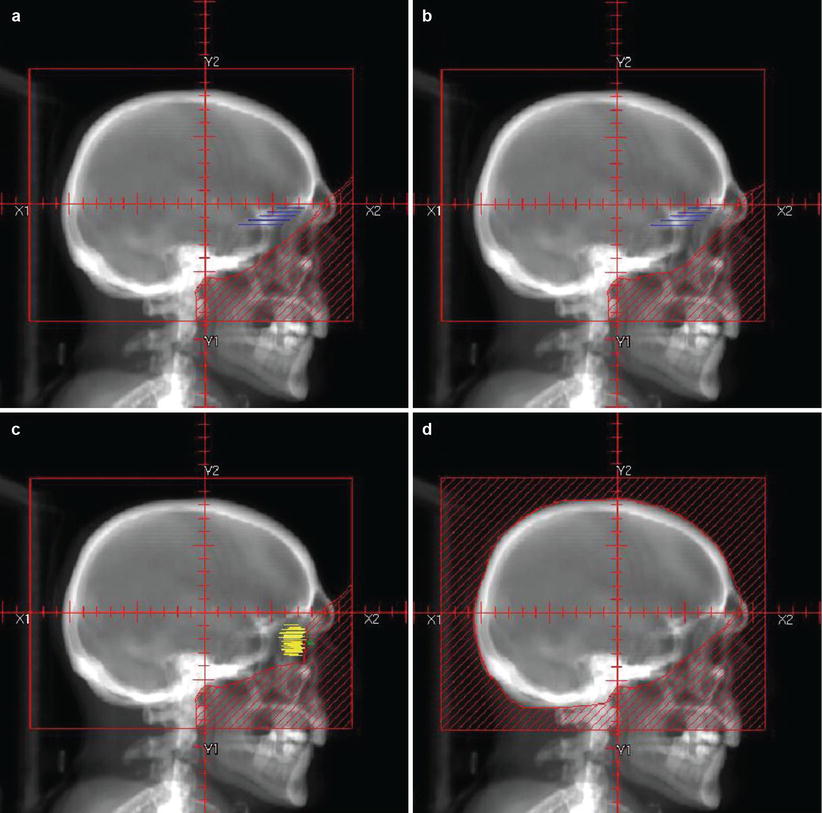

Fig. 2
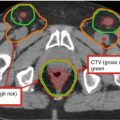
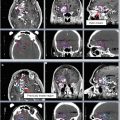
Variations on WBRT fields. (a) Conventional fields (RAO/LAO) as described in Fig. 1. (b) More generous WBRT fields used in the setting of leptomeningeal disease – these fields provide additional margin on the cribriform plate (blue). (c) Conventional fields (RAO/LAO) covering the traditional WBRT target with the addition of coverage of the bilateral retinas (yellow) in the setting of proven retinal involvement (e.g., CNS lymphoma, CNS prophylaxis for leukemia, leukemic infiltrate to the retina) with blocking of the lens (green) and anterior chamber. (d) Scalp-sparing WBRT fields – the block edge is set at the outer table of the calvarium to minimize alopecia in patients for whom cosmesis is of particular concern. The blocked field is represented by the diagonal red lines
A wide variety of dose and fractionation schemes are used for WBRT, with 30 Gy in 10 fractions being the most common. For patients with a relatively long life expectancy (and greater concern for neurocognitive sequelae), more protracted fractionation schemes (30 Gy in 12 fractions, 37.5 in 15 fractions) can be considered. The most commonly recommended dose for PCI in SCLC is 25 Gy in 10 daily fractions. For CNS leukemia, a total dose of 18–24 Gy is given at 1.8 Gy per fraction.
For lymphoreticular involvement, radiation fields should include the posterior 1/3 of the orbit and cribriform plate (Fig. 2).
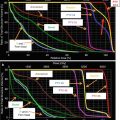
IMRT can be used for HA-WBRT (Fig. 3). The standard dose scheme is 30 Gy in 10 fractions with a maximal hippocampal dose of 10 Gy. The CTV is defined as the entire brain parenchyma. The PTV is defined as the CTV minus the hippocampus + 3–5 mm volumetric expansion. Hippocampus contouring is best seen on T1 series MRI to identify the gray matter in the medial temporal horn. The RTOG atlas (see suggested reading) is available for further guidance.


Fig. 3
Hippocampal avoidance WBRT. Axial slices are presented from caudal (a) to cranial (d) extent with CT and matched T1 series MRI. Structures highlighted include the hippocampal formation of interest (red), expansion (blue), normal brain tissue (khaki), and brain stem (black). The CTV contains all normal brain tissue with the hippocampal formation expansion removed from the target
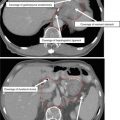
Reirradiation is done on a selective basis with a lowered total dose of 20–25 Gy in 10 fractions and a time interval of at least 4–6 months between the initial and repeat course. Blocking radiosensitive organ at risk (OAR) structures, including the optic nerve and chiasm, is accomplished by creating a block with a 3 mm expansion on the OAR, as demonstrated in Fig. 4.


Fig. 4
Reirradiation using a peninsula block. (a) Optic nerves (pink) and chiasm (green) are blocked with a 3 mm OAR PTV (purple). A standard WBRT is modified to include a block covering the PTV as well as the spinal cord caudal to the brain stem (black). Axial slices from caudal (b) to cranial (d) are shown with MLC blocks from the RAO beam (red) and LAO beam (green)
4.2 SRS
The optimal use of SRS in conjunction with WBRT or as stand-alone treatment remains controversial. Randomized data supports the addition of SRS before or after WBRT for patients with 1–3 metastases (Andrews et al. 2004). SRS alone may also be offered to patients with 1–3 lesions (Chang et al. 2009; Aoyama et al. 2006), provided that close imaging follow-up can be obtained to monitor for additional disease.
SRS is generally appropriate for lesions less than 4 cm in largest diameter. Independent of size, neurosurgical management may be preferred for lesions causing symptoms and mass effect. Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in 3–5 fractions is preferred for larger lesions.
For frame-based SRS, the gross tumor volume (GTV) is contoured as the visualized lesion on contrast-enhanced MRI (Fig. 5). No CTV or PTV expansions are used (in frameless systems, a 1–2 mm PTV expansion should be created depending on the setup accuracy). Dose is typically prescribed to the 50 % isodose line for Gamma Knife and 75–95 % for LINAC-based SRS, with the choice of prescription dose determined by lesion size (Table 1). SRS can create a highly conformal dose distribution, allowing for treatment of lesions in close proximity to critical OAR structures (Fig. 6); however, care must be paid to normal tissue tolerance (Table 2).