(1)
Department of Radiology, John H Stroger Jr Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL, USA
Noninfectious Aortitis
Diagnosis
Takayasu Vasculitis
Imaging Features
1.
Affects large vessels with predilection for the aorta and its branch vessels and young or middle-aged females.
2.
Noncontrast study shows high attenuation of aortic or pulmonary artery wall, CECT shows concentric thickening of the vessel wall and double ring of the aorta in early disease.
3.
Stenosis is common, also occlusion, thrombosis, ectasia, aneurysms, and ulcers.
4.
Arterial wall calcification in chronic cases.
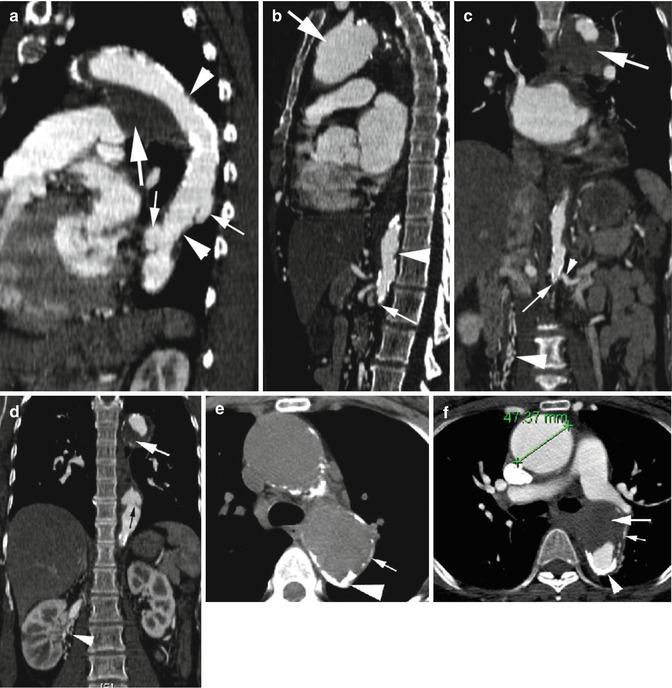
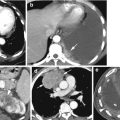
Fig. 5.1
Takayasu arteritis—late phase. (a) Sagittal reformatted CT shows stenosis of mid-arch of the aorta and proximal descending aorta (arrowheads) with large chronic intramural thrombus (thick arrow) at the arch. The proximal descending aorta shows two saccular aneurysms (thin arrows). (b) Sagittal reformatted CT shows aneurysm of the ascending aorta (thick arrow), focal stenosis of the proximal abdominal aorta (arrowhead), and complete occlusion of the aorta distal to renal arteries (thin arrow). (c) Coronal reformatted images show complete occlusion of the aorta (thin arrow) distal to the origin of renal arteries (thin arrowhead) and dilated collateral arteries mostly medial to the right kidney (thick arrowhead). Mural thrombus is again seen around proximal arch of the aorta (thick arrow). (d) Coronal reformatted image shows concentric stenosis of distal thoracic aorta (black arrow). Large intramural thrombus at arch (white arrow) and collateral vessels adjacent to the right kidney (arrowhead) are again seen. (e, f) Pre- and postcontrast axial images show aneurysm of the ascending aorta (caliper) and thick, rough transmural degenerative atherosclerotic calcification (thick arrowhead) and thin dystrophic calcification (thin white arrow) and large focal chronic intramural hematoma in posterior arch (thick arrow)
Diagnosis
Giant Cell Arteritis
Imaging Features
1.
Affects large- and medium-sized vessels in individuals over 50 years
2.
Predominantly affects extracranial carotid branches especially the temporal arteries, aorta, and rarely central pulmonary arteries
3.
Similar to Takayasu arteritis with wall thickening, stenosis, and aneurysm formation
4.
Aneurysms more frequent in the thoracic aorta and prone to dissection
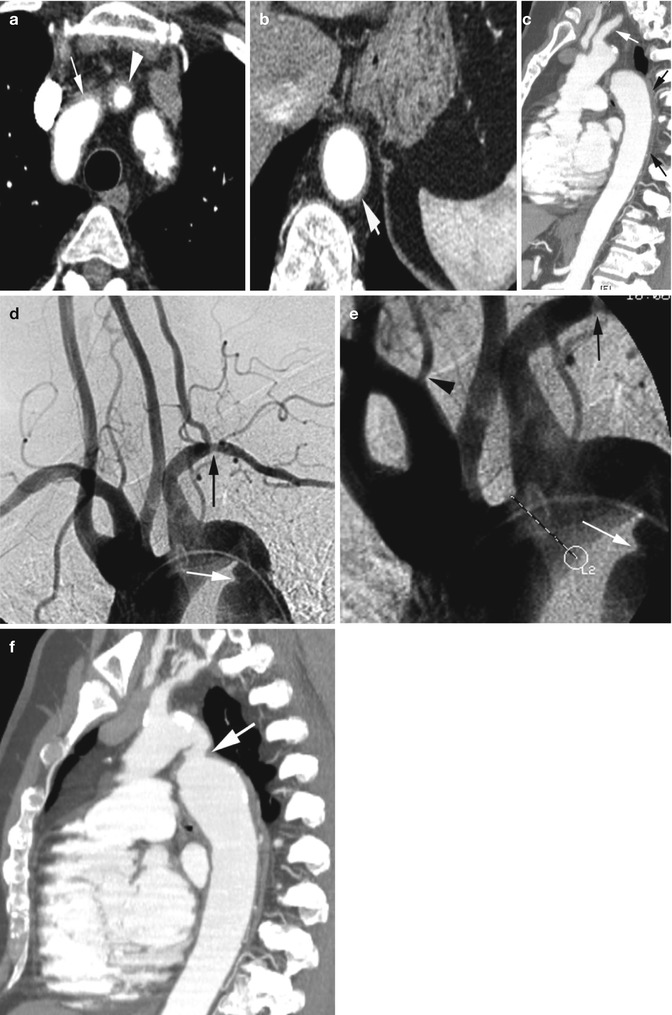
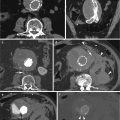
Fig. 5.2
Giant cell arteritis in a 70-year-old woman. (a, b) Axial CT angiogram shows diffuse wall thickening of anterior arch (arrow), origin of left common carotid (arrowhead) and distal thoracic aorta (short arrow). (c) Sagittal reformatted image shows diffuse wall thickening of the left subclavian artery (white arrow) and descending thoracic aorta (black arrows). (d, e) Angiogram shows stenosis of left subclavian artery (black arrow), mild narrowing at origin of right vertebral artery (arrowhead), and stenosis of distal arch of the aorta (white arrow). (f) Sagittal reformatted CT angiogram shows stenosis of distal arch of the aorta (arrow)
Diagnosis
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener Granulomatosis)
Imaging Features
1.
Vasculitis primarily of small- to medium-sized vessels can also have aortitis and periaortitis.
2.
Granulomatous inflammation of upper and lower respiratory tracts and glomerulonephritis.
3.
Pulmonary nodules, multiple, bilateral, and tend to cavitation.
4.
Pulmonary infiltrates (waxing and waning), hemorrhage or edema, and hilar lymphadenopathy.
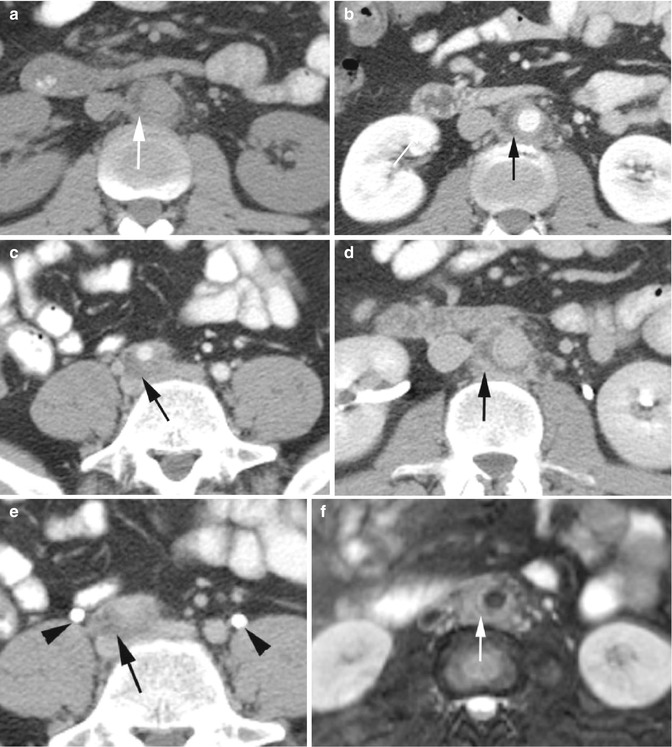
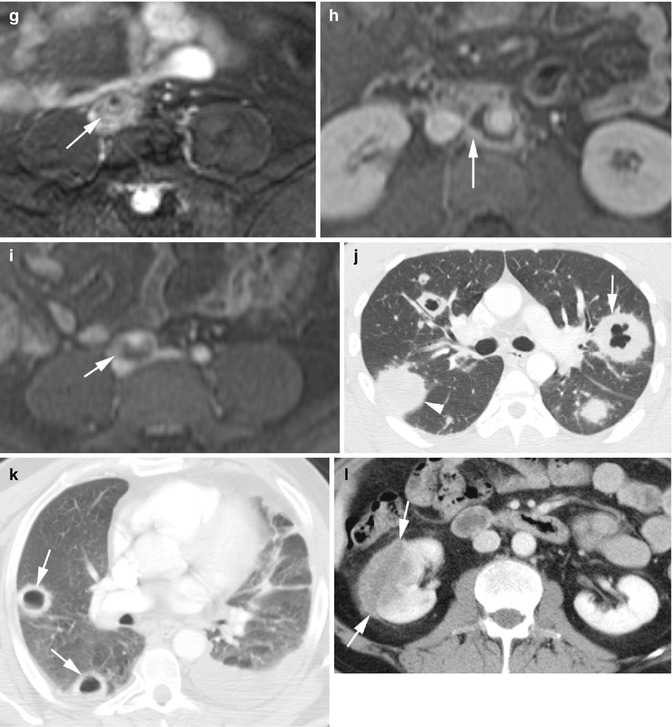
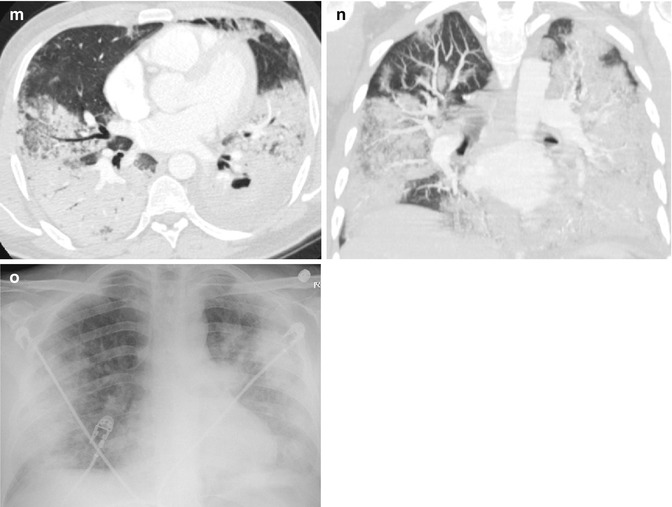
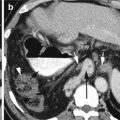
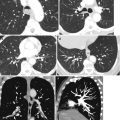
Fig. 5.3




Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (a) precontrast axial CT shows layered soft tissue around infrarenal aorta with central lower density (arrow). (b, c) Postcontrast axial CT again shows layered soft tissue around the infrarenal aorta and right common iliac artery with no significant enhancement of the peripheral rind (arrow). (d) Delayed phase axial CT shows mild enhancement of the peripheral rim of inflammatory tissue around the abdominal aorta (arrow). (e) Delayed-phase axial CT shows the ureters in their usual location (arrowheads) and separate from the inflammatory tissue around the common iliac artery (arrow). (f, g) T2 fat-sat axial MRI of the infrarenal aorta and right common iliac artery shows high signal intensity in soft tissue around the vessels (arrow). (h, i) Post-gad axial MRI shows appreciable enhancement of the rind surrounding the necrotic tissue around the vessels (arrow). (j, k) Axial CT of two patients with known Wegener granulomatosis show multiple bilateral pulmonary nodules. (j) Thick-walled cavitating nodules (arrow) and solid nodules (arrowhead). (k) Thinner-walled cavitating nodules (arrows). (l) Axial CT of the same patient in (k) shows focal glomerulonephritis of the right kidney showing low-density mass with poor enhancement (arrows). (m–o) Axial and coronal reformatted CT and chest X-ray of a known case of Wagner granulomatosis showing bilateral diffuse pulmonary hemorrhage with ground-glass densities and consolidations
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree