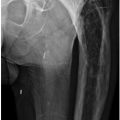
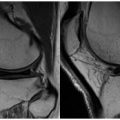
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
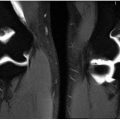
2b The patient is scheduled for an arthrogram followed by a CT examination of the left shoulder. What is the most appropriate mixture for the arthrogram?
A. Iodinated contrast 1:1 saline and/or anesthetic
B. Iodinated contrast 1:10 saline and/or anesthetic
C. Iodinated contrast 1:100 saline and/or anesthetic
D. Iodinated contrast 1:1,000 saline and/or anesthetic
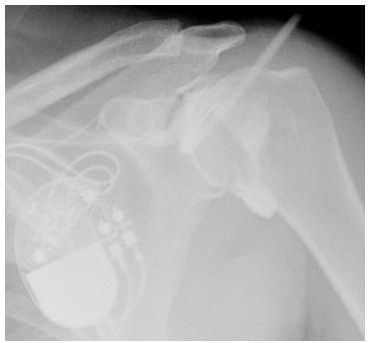
2c Which of the following is an appropriate reason for a CT arthrogram instead of MRI arthrogram?
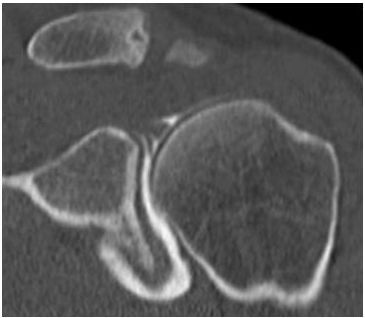
A. Lack of joint mobility
B. Anticoagulation
C. Infection at the injection site
D. Metallic hardware near the joint
3 Placing an MRI receiver coil farther than normal from the area of interest will result in
A. increased signal-to-noise ratio.
B. decreased receiver bandwidth.
C. decreased spatial resolution.
D. decreased signal-to-noise ratio.
4 You are called to evaluate a patient following inadvertent IV contrast infiltration. The technologist informs you that ~100 mL of iodinated contrast extravasated into the antecubital fossa. Which of the following is the primary clinical concern?
A. Compartment syndrome
B. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis
C. Contrast-related renal dysfunction
D. Vasospasm
5 What percentage of bone mineralization must be lost to be detected by radiographs?
A. 10% to 20%
B. 30% to 40%
C. 50% to 60%
D. 70% to 80%
6a A patient presents for a left hip arthrogram. What is the preferred needle location to avoid complications with nerve, vessel, and bursa injections?
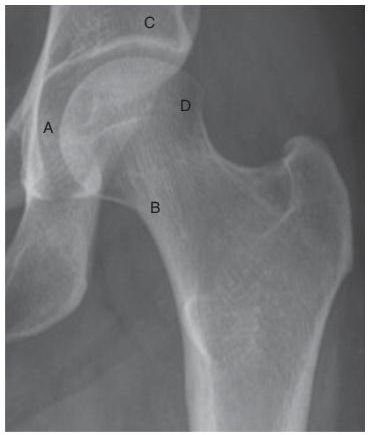
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
6b The patient is scheduled for an arthrogram followed by an MRI examination of the left hip. What is the appropriate mixture for the arthrogram?
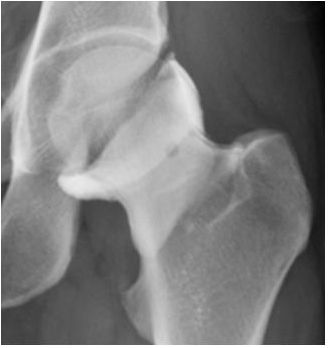
A. 0.01 mL gadolinium per 20 mL of iodinated contrast, saline, and/or anesthetic mixture
B. 0.1 mL gadolinium per 20 mL of iodinated contrast, saline, and/or anesthetic mixture
C. 1 mL gadolinium per 20 mL of iodinated contrast, saline, and/or anesthetic mixture
D. 10 mL gadolinium per 20 mL of iodinated contrast, saline, and/or anesthetic mixture
6c For which of the following scenarios is MRI preferred over CT after arthrography?
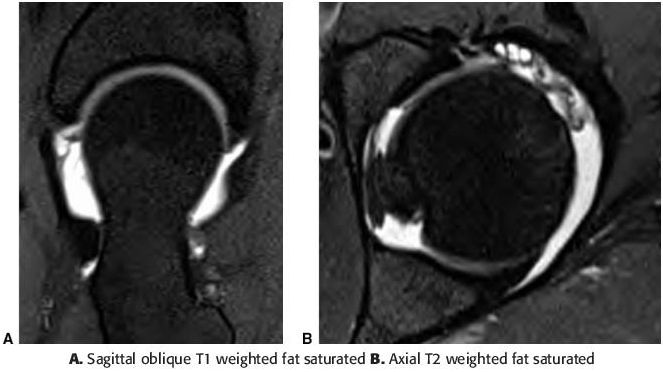
A. Claustrophobic patient
B. Potential cartilage defects
C. Obese patients
D. Prior labral surgery
7 The following image shows an artifact. From the list below select the best protocol change to eliminate this artifact.
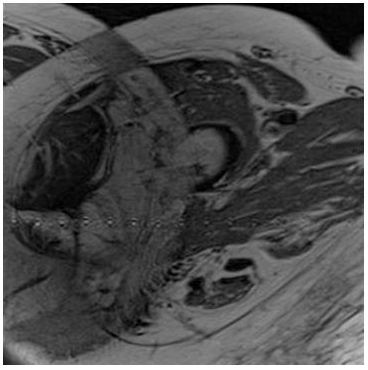
A. Double the image matrix.
B. Double the image oversampling in the phase-encoded direction.
C. Double the receiver bandwidth.
D. Double the FOV.
8 Fluid appears as increased signal on a T2-weighted image because it has which of the following?
A. Short T2 relaxation time
B. Short T1 relaxation time
C. Long T2 relaxation time
D. Long T1 relaxation time
9 Which of the following will achieve high-resolution imaging of small MSK structures?
A. Use 2D imaging with thin slices.
B. Use 3D imaging with thin slices.
C. Use 2D imaging with a large number of averages.
D. Use proton density imaging.
10 Which of the following would be the best method to achieve quality T2-weighted images in a patient with difficulty remaining still during imaging?
A. Use single-echo spin echo imaging.
B. Use gradient-echo imaging.
C. Use a radial imaging such as BLADE (MRI acronym, Siemens) or PROPELLOR (MRI acronym, GE).
D. Use the body coil instead of a surface coil.
11 What artifact is noted on the sagittal T2-weighted MR image below?
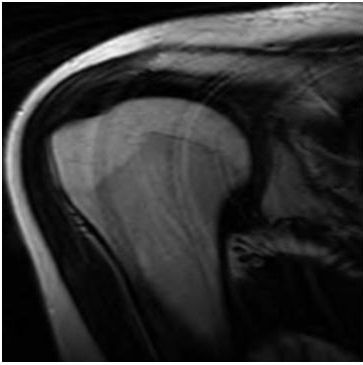
A. Gibbs phenomenon
B. Chemical shift
C. Motion
D. Wraparound
12 Injecting a gadolinium contrast agent causes a sarcoma to
A. appear bright on T1-weighted images.
B. appear dark on T2-weighted images.
C. appear isointense to skeletal muscle on T1-weighted images.
D. appear bright on proton density–weighted images.
13 Which of the following parameters can be altered without changing the total scan time?
A. Number of excitations (NEX)
B. Number of phase-encoding steps
C. number of frequency encoding steps
D. Time of repetition (TR)
E. Echo train length (ETL)
14 Which of the following would cause a lower signal-to-noise ratio on a T2-weighted image?
A. Increase the number of averages
B. Increase the bandwidth
C. Decrease the echo time (TE)
D. Decrease the echo train interval
15 A patient has a large, dark-colored tattoo over the area that needs to undergo an MRI examination. Which of the following is a likely safety concern?
A. Interference with scan
B. Susceptibility distortion
C. Heating of the tattoo by radio waves
D. Heating of the tattoo by gradients
16 The following image of a pelvis has an artifact. What is the most likely cause?
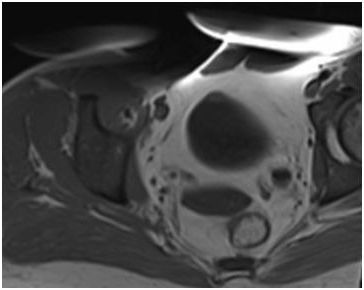
A. Aliasing of signal from posterior soft tissues
B. Metal-induced field distortion
C. Poor fat suppression
D. Patient movement
17 Why is fluid surrounding the joint hyperintense on this T1-weighted image?
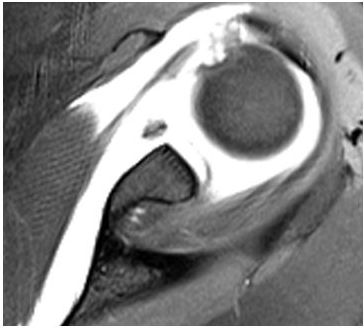
A. Saline was injected into the joint.
B. Omnipaque was injected into the joint.
C. Gadolinium was injected into the joint.
D. It is an inflow artifact.
18 A 50-year-old male on dialysis presents with findings concerning for osteomyelitis of the foot, and an MRI has been ordered for further characterization. What dose of gadolinium contrast is recommended?
A. 0.1 mmol/kg
B. 0.05 mmol/kg
C. 0.01 mmol/kg
D. 0 mmol/kg
19 This image of an arm was acquired on a subject with metal in the same arm. Which of the following would exacerbate the artifact?

A. Long echo time (TE) gradient-echo sequence
B. Fast/turbo spin echo sequence
C. Short echo time (TE) spin echo sequence
D. Increasing the bandwidth
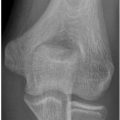
20 In the image below, the bright signal surrounding the fracture of the distal tibia is best described as which of the following?
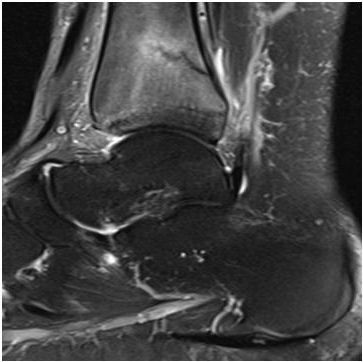
A. Increased T1 signal
B. Increased T2 signal
C. Decreased T1 signal
D. Decreased T2 signal
21 A 35-year-old female undergoes a CT examination with contrast and develops severe bronchospasm. What should you administer?
A. 1 to 3 mL of 1/10,000 dilution of epinephrine IM
B. 1 to 3 mL of 1/10,000 dilution of epinephrine IV
C. 0.3 mL of 1/10,000 dilution of epinephrine IM
D. 0.3 mL of 1/10,000 dilution of epinephrine IV
22 Which of the following is an advantage of performing a biopsy of a soft tissue mass under ultrasound guidance?
A. Allows for the shortest passage of the needle to the target
B. Eliminates the need for conscious sedation
C. Areas of vascularity and viable tissue can be assessed throughout the procedure
D. Allows for use of a smaller gauge biopsy needle
23 Which of the following tumor locations should be biopsied under CT guidance without consideration for ultrasound guidance?
A. Intramedullary
B. Subperiosteal
C. Cortical
D. Soft tissue
24 A 26-year-old male with bacterial endocarditis develops hip pain while in the hospital. A hip aspiration is ordered to evaluate for a septic hip. Which option below represents the most appropriate needle placement for the aspiration?
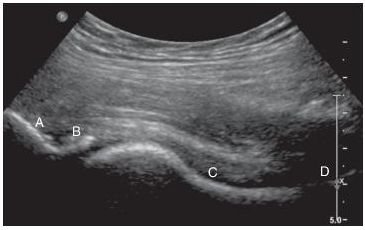
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
25 A 20-year-old male endures a wrist injury after a fall. Which of the following studies would offer the best spatial resolution to detect a subtle fracture of the scaphoid cortex?
A. STIR axial images
B. Thin-section CT
C. T1-weighted axial images
D. Bone scan
26 A 75-year-old female with osteoporosis injures her hip after a fall. Which of the following studies would offer the best contrast resolution to evaluate for a nondisplaced fracture of the hip?
A. Radiographs
B. CT
C. MRI
D. Ultrasound
27 A 45-year-old male presents with shoulder pain after sustaining an injury playing tennis. Which of the following studies would offer the best spatial resolution of the rotator cuff tendons?
A. Bone scan
B. CT
C. MRI
D. Ultrasound
28a A 60-year-old female presents with the dual x-ray absorptiometry study of the hip presented below. Based on the results of this study, what diagnosis would this patient receive?
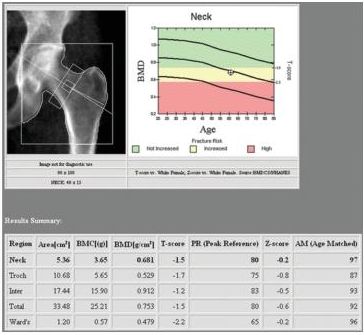
A. Normal
B. Osteomalacia
C. Osteopenia
D. Osteoporosis
28b What is the difference between the T-score and the Z-score?
A. The T-score is the absolute bone mineral density score.
B. The T-score is calculated by comparing the patient to a young-normal reference population.
C. The Z-score is the absolute bone mineral density score.
D. The Z-score is calculated by comparing the patient to a young-normal reference population.
29 Which of the following is the most appropriate use of F-18 FDG PET/CT for evaluation of soft tissue tumors?
A. Evaluation of treatment response
B. Biopsy needle placement planning
C. Initial formation of a differential diagnosis
D. Screening of at-risk family members
30 A 45-year-old male presents with clinical concern for vertebral osteomyelitis. The patient has an MRI-incompatible implanted device. Which of the following studies below is suggested for evaluation of vertebral osteomyelitis?
A. Tc-99m MDP
B. Tc-99m HMPAO
C. Ga-67 citrate
D. In-111 WBC
31 A 50-year-old female presents with clinical concern for an infected right knee prosthesis. Which of the following scenarios would be diagnostic for infection?
A. Tc-99m sulfur colloid uptake exceeds In-111 WBC uptake.
B. In-111 WBC uptake exceeds Tc-99m sulfur colloid uptake.
C. Tc-99m sulfur colloid uptake equals In-111 WBC uptake.
D. In-111 WBC has increased uptake without comparison to Tc-99m sulfur colloid.
32 Typically, no grid is used when acquiring extremity radiographs. Which of the following is the best explanation?
A. The use of the grid will block primary x-rays.
B. The use of the grid will degrade image quality.
C. Scatter radiation is not significant in imaging the hand and foot.
D. The use of the grid will decrease patient dose.
33 For anterior to posterior (AP) imaging of the pelvis, which of the following osseous edges will be the sharpest, that is, that has the least blurring (unsharpness)?
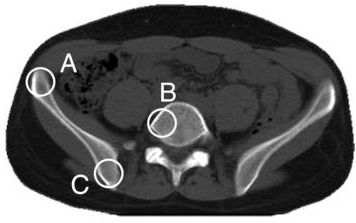
A. A, since it has the longest object to detector distance
B. B, since it is located at the center of the x-ray beam
C. C, since it has the shortest object to detector distance
D. The same, since the focal spot blurring is independent of the location
34
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree